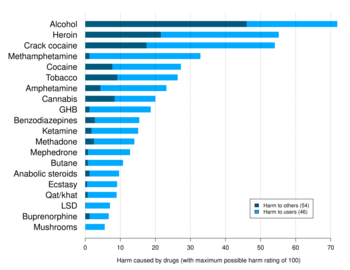
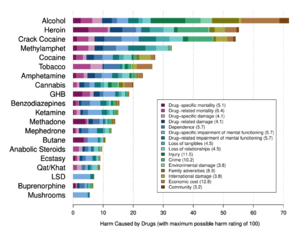
Chemistry:Alcoholic drink


An alcoholic drink (or alcoholic beverage) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of alcohol produced by fermentation of grains, fruits, or other sources of sugar. The consumption of alcohol plays an important social role in many cultures. Most countries have laws regulating the production, sale, and consumption of alcoholic beverages.[2] Some countries ban such activities entirely, but alcoholic drinks are legal in most parts of the world. The global alcoholic drink industry exceeded $1 trillion in 2018.[3]
Alcohol is a depressant, which in low doses causes euphoria, reduces anxiety, and improves sociability. In higher doses, it causes drunkenness, stupor, unconsciousness, or death. Long-term use can lead to alcohol abuse, cancer, physical dependence, and alcoholism. Alcohol is one of the most widely used recreational drugs in the world, with about 33% of people being current drinkers.[4] (As of 2016), women on average drink 0.7 drinks and males 1.7 drinks a day.[4] In 2015, among Americans, 86% of adults had consumed alcohol at some point, 70% had drunk it in the last year, and 56% in the last month.[5] Alcoholic drinks are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and spirits—and typically their alcohol content is between 3% and 50%.
Discovery of late Stone Age jugs suggest that intentionally fermented drinks existed at least as early as the Neolithic period (cir. 10,000 BC).[6] Many animals also consume alcohol when given the opportunity and are affected in much the same way as humans, although humans are the only species known to produce alcoholic drinks intentionally.[7]
Fermented drinks
Beer
Beer is a beverage fermented from grain mash. It is typically made from barley or a blend of several grains and flavored with hops. Most beer is naturally carbonated as part of the fermentation process. If the fermented mash is distilled, then the drink becomes a spirit. In the Andean region, the most common beer is chicha, made from grain or fruits.[8] Beer is the most consumed alcoholic beverage in the world.[9]
Cider
Cider or cyder (/ˈsaɪdər/ SY-dər) is a fermented alcoholic drink made from any fruit juice; apple juice (traditional and most common), peaches, pears ("Perry" cider) or other fruit. Cider alcohol content varies from 1.2% ABV to 8.5% or more in traditional English ciders. In some regions, cider may be called "apple wine".[10]
Mead
Mead (/miːd/) is an alcoholic drink made by fermenting honey with water, sometimes with various fruits, spices, grains, or hops. The alcoholic content of mead may range from about 8% ABV to more than 20%. The defining characteristic of mead is that the majority of the drink's fermentable sugar is derived from honey.
Pulque
Pulque is the Mesoamerican fermented drink made from the "honey water" of maguey, Agave americana. The drink distilled from pulque is tequila or mescal Mezcal.[11]
Wine
Wine is a fermented beverage produced from grapes and sometimes other fruits. Wine involves a longer fermentation process than beer and a long aging process (months or years), resulting in an alcohol content of 9%–16% ABV.
"Fruit wines" are made from fruits other than grapes, such as plums, cherries, or apples.
Sake is a popular example of "rice wine".
Sparkling wine like French Champagne, Catalan Cava or Italian Prosecco can be made by means of a secondary fermentation.
Distilled drinks

A distilled drink or liquor is an alcoholic drink produced by distilling (i.e., concentrating by distillation) ethanol produced by means of fermenting grain, fruit, or vegetables.[12] Unsweetened, distilled, alcoholic drinks that have an alcohol content of at least 20% ABV are called spirits.[13] For the most common distilled drinks, such as whiskey and vodka, the alcohol content is around 40%. The term hard liquor is used in North America to distinguish distilled drinks from undistilled ones (implicitly weaker). Vodka, gin, baijiu, tequila, whiskey, brandy, and soju are examples of distilled drinks. Distilling concentrates the alcohol and eliminates some of the congeners. Freeze distillation concentrates ethanol along with methanol and fusel alcohols (fermentation by-products partially removed by distillation) in applejack.
Fortified wine is wine, such as port or sherry, to which a distilled beverage (usually brandy) has been added.[14] Fortified wine is distinguished from spirits made from wine in that spirits are produced by means of distillation, while fortified wine is simply wine that has had a spirit added to it. Many different styles of fortified wine have been developed, including port, sherry, madeira, marsala, commandaria, and the aromatized wine vermouth.[15]
Rectified spirit
Rectified spirit, also called "neutral grain spirit", is alcohol which has been purified by means of "rectification" (i.e. repeated distillation). The term neutral refers to the spirit's lack of the flavor that would have been present if the mash ingredients had been distilled to a lower level of alcoholic purity. Rectified spirit also lacks any flavoring added to it after distillation (as is done, for example, with gin). Other kinds of spirits, such as whiskey, are distilled to a lower alcohol percentage to preserve the flavor of the mash.
Rectified spirit is a clear, colorless, flammable liquid that may contain as much as 95% ABV. It is often used for medicinal purposes. It may be a grain spirit or it may be made from other plants. It is used in mixed drinks, liqueurs, and tinctures, and also as a household solvent.
Health effects
Alcohol has significant negative health effects, including increased risk of death and cancer.[4] Negative effects are related to the amount consumed with no safe lower limit seen.[4]
Short-term effects
Wine, beer, distilled spirits and other alcoholic drinks contain ethyl alcohol and alcohol consumption has short-term psychological and physiological effects on the user. Different concentrations of alcohol in the human body have different effects on a person. The effects of alcohol depend on the amount an individual has drunk, the percentage of alcohol in the wine, beer or spirits and the timespan that the consumption took place, the amount of food eaten and whether an individual has taken other prescription, over-the-counter or street drugs, among other factors. Alcohol in carbonated drinks is absorbed faster than alcohol in non-carbonated drinks.[16]
Drinking enough to cause a blood alcohol concentration (BAC) of 0.03–0.12% typically causes an overall improvement in mood and possible euphoria, increased self-confidence and sociability, decreased anxiety, a flushed, red appearance in the face and impaired judgment and fine muscle coordination. A BAC of 0.09% to 0.25% causes lethargy, sedation, balance problems and blurred vision. A BAC from 0.18% to 0.30% causes profound confusion, impaired speech (e.g., slurred speech), staggering, dizziness and vomiting. A BAC from 0.25% to 0.40% causes stupor, unconsciousness, anterograde amnesia, vomiting (death may occur due to inhalation of vomit (pulmonary aspiration) while unconscious) and respiratory depression (potentially life-threatening). A BAC from 0.35% to 0.80% causes a coma (unconsciousness), life-threatening respiratory depression and possibly fatal alcohol poisoning. Alcohol is eliminated by enzymes in the liver at a rate of ca. 15 mg per dL of blood per hour (mg/dL/h).[17] For a 100 kg man, this corresponds to ca. 15 mL per hour, which is the pure alcohol content of a typical 300 mL small beer bottle.[18] The rate of elimination depends linearly on body weight and follows zero order kinetics, but can be doubled by repeated exposure (habitual drinking).
Drinking while driving, operating aircraft, watercraft or heavy machinery increases the risk of an accident and is often a separately defined felony punishable by jail, license suspension, fines or compulsory treatment.
Long-term effects

Alcohol is the main active ingredient of wine, beer and distilled spirits. Drinking small quantities of alcohol (less than one drink in women and two in men per day) is associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes mellitus, and early death.[20] Drinking more than this amount, however, increases the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, and stroke.[20] The risk is greater in younger people due to binge drinking, which may result in violence or accidents.[20] About 3.3 million deaths (5.9% of all global deaths) are believed to be due to alcohol each year.[5] Alcoholism reduces a person's life expectancy by around ten years[21] and alcohol use is the third leading cause of early death in the United States.[20] Even moderate alcohol consumption increases cancer risk in individuals.[22][23] No professional medical association recommends that people who are non-drinkers should start drinking wine.[20][24] Another long-term effect of alcohol usage, when also used with tobacco products, is alcohol acting as a solvent, which allows harmful chemicals in tobacco to get inside the cells that line the digestive tract. Alcohol slows these cells' healing ability to repair the damage to their DNA caused by the harmful chemicals in tobacco. Alcohol contributes to cancer through this process.[25]
While lower quality evidence suggests a cardioprotective effect, no controlled studies have been completed on the effect of alcohol on the risk of developing heart disease or stroke. Excessive consumption of alcohol can cause liver cirrhosis and alcoholism.[26] The American Heart Association "cautions people NOT to start drinking ... if they do not already drink alcohol. Consult your doctor on the benefits and risks of consuming alcohol in moderation."[27]
Alcoholic drinks are classified by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) as a Group 1 carcinogen (carcinogenic to humans). IARC classifies alcoholic drink consumption as a cause of female breast, colorectum, larynx, liver, esophagus, oral cavity, and pharynx cancers; and as a probable cause of pancreatic cancer.[28]
Congeners
In the alcoholic drinks industry, congeners are substances produced during fermentation. These substances include small amounts of chemicals such as occasionally desired other alcohols, like propanol and 3-methyl-1-butanol, but also compounds that are never desired such as acetone, acetaldehyde and glycols. Congeners are responsible for most of the taste and aroma of distilled alcoholic drinks, and contribute to the taste of non-distilled drinks.[29] It has been suggested that these substances contribute to the symptoms of a hangover.[30] Tannins are congeners found in wine in the presence of phenolic compounds. Wine tannins add bitterness, have a drying sensation, taste herbaceous and are often described as astringent. Wine tannins adds balance, complexity, structure and makes a wine last longer, so they play an important role in the aging of wine.[31]
Food energy
Alcoholic drinks are a source of food energy. The USDA uses a figure of 6.93 kilocalories (29.0 kJ) per gram of alcohol (5.47 kcal or 22.9 kJ per ml) for calculating food energy.[32] In addition to alcohol, many alcoholic drinks contain carbohydrates. For example, in 12 US fl oz (355 ml) of 5% ABV beer, along with approximately 18 ml of alcohol (96 kilocalories or 400 kilojoules), there are usually 10–15 g of carbohydrates (about 40–60 kcal or 170–250 kJ).[citation needed] Excessive daily calorie intake may contribute to an increase in body weight and "beer belly". In addition to the direct effect of its caloric content, alcohol is also known to potentiate the insulin response of the human body to glucose, which, in essence, "instructs" the body to convert consumed carbohydrates into fat and to suppress carbohydrate and fat oxidation.[33][34] Ethanol is directly processed in the liver to acetyl CoA, the same intermediate product as in glucose metabolism. Because ethanol is mostly metabolized and consumed by the liver, chronic excessive use can lead to fatty liver. This leads to a chronic inflammation of the liver and eventually alcoholic liver disease.
Amount of use
The average number of people who drink (As of 2016) was 39% for males and 25% for females (2.4 billion people in total).[4] Females on average drink 0.7 drinks per day while males drink 1.7 drinks per day.[4] The rates of drinking varies significantly in different areas of the world.[4]
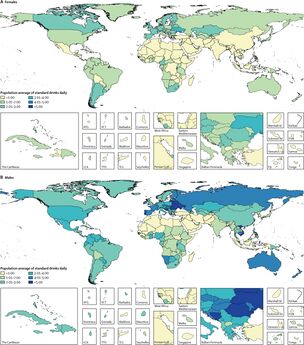
Age-standardised prevalence of current drinking for females (A) and males (B) in 2016, in 195 locations.[4]
Average standard drinks (10 g of pure ethanol per serving) consumed per day, age-standardised, for females (A) and males (B) in 2016, in 195 locations.[4]
Reasons for use
Apéritifs and digestifs
An apéritif is any alcoholic beverage usually served before a meal to stimulate the appetite,[35] while a digestif is any alcoholic beverage served after a meal for the stated purpose of improving digestion. Fortified wine, liqueurs, and dry champagne are common apéritifs. Because apéritifs are served before dining, they are usually dry rather than sweet. One example is Cinzano, a brand of vermouth. Digestifs include brandy, fortified wines and herb-infused spirits (Drambuie).
Flavoring
Pure ethanol tastes bitter to humans; some people also describe it as sweet.[36] However, ethanol is also a moderately good solvent for many fatty substances and essential oils. This facilitates the use of flavoring and coloring compounds in alcoholic drinks as a taste mask, especially in distilled drinks. Some flavors may be naturally present in the beverage's raw material. Beer and wine may also be flavored before fermentation, and spirits may be flavored before, during, or after distillation. Sometimes flavor is obtained by allowing the beverage to stand for months or years in oak barrels, usually made of American or French oak. A few brands of spirits may also have fruit or herbs inserted into the bottle at the time of bottling.
Wine is important in cuisine not just for its value as an accompanying beverage, but as a flavor agent, primarily in stocks and braising, since its acidity lends balance to rich savory or sweet dishes.[37] Wine sauce is an example of a culinary sauce that uses wine as a primary ingredient.[38] Natural wines may exhibit a broad range of alcohol content, from below 9% to above 16% ABV, with most wines being in the 12.5–14.5% range.[39] Fortified wines (usually with brandy) may contain 20% alcohol or more.
Alcohol measurement
Alcohol concentration
| Beers | typically 5% (range is from 3–15%) |
| Wines | typically 13.5% (range is from 8%–17%) |
| Fortified wines | 15–22% |
| Spirits | typically 30%-40% (range is from 15% to, in some rare cases, up to 98%) |
| Fruit juices | < 0.1% |
| Cider, wine coolers | 4%–8% |
The concentration of alcohol in a beverage is usually stated as the percentage of alcohol by volume (ABV, the number of milliliters (ml) of pure ethanol in 100 ml of beverage) or as proof. In the United States, proof is twice the percentage of alcohol by volume at 60 degrees Fahrenheit (e.g. 80 proof = 40% ABV). Degrees proof were formerly used in the United Kingdom, where 100 degrees proof was equivalent to 57.1% ABV. Historically, this was the most dilute spirit that would sustain the combustion of gunpowder.
Ordinary distillation cannot produce alcohol of more than 95.6% by weight, which is about 97.2% ABV (194.4 proof) because at that point alcohol is an azeotrope with water. A spirit which contains a very high level of alcohol and does not contain any added flavoring is commonly called a neutral spirit. Generally, any distilled alcoholic beverage of 170 US proof or higher is considered to be a neutral spirit.[41]
Most yeasts cannot reproduce when the concentration of alcohol is higher than about 18%, so that is the practical limit for the strength of fermented drinks such as wine, beer, and sake. However, some strains of yeast have been developed that can reproduce in solutions of up to 25% ABV.[42]
Serving measures
Shot sizes
Shot sizes vary significantly from country to country. In the United Kingdom, serving size in licensed premises is regulated under the Weights and Measures Act (1985). A single serving size of spirits (gin, whisky, rum, and vodka) are sold in 25 ml or 35 ml quantities or multiples thereof.[43] Beer is typically served in pints (568 ml), but is also served in half-pints or third-pints. In Israel, a single serving size of spirits is about twice as much, 50 or 60 mL.
The shape of a glass can have a significant effect on how much one pours. A Cornell University study of students and bartenders' pouring showed both groups pour more into short, wide glasses than into tall, slender glasses.[44] Aiming to pour one shot of alcohol (1.5 ounces or 44.3 ml), students on average poured 45.5 ml & 59.6 ml (30% more) respectively into the tall and short glasses. The bartenders scored similarly, on average pouring 20.5% more into the short glasses. More experienced bartenders were more accurate, pouring 10.3% less alcohol than less experienced bartenders. Practice reduced the tendency of both groups to over pour for tall, slender glasses but not for short, wide glasses. These misperceptions are attributed to two perceptual biases: (1) Estimating that tall, slender glasses have more volume than shorter, wider glasses; and (2) Over focusing on the height of the liquid and disregarding the width.
Standard drinks
A standard drink is a notional drink that contains a specified amount of pure alcohol. The standard drink is used in many countries to quantify alcohol intake. It is usually expressed as a measure of beer, wine, or spirits. One standard drink always contains the same amount of alcohol regardless of serving size or the type of alcoholic beverage. The standard drink varies significantly from country to country. For example, it is 7.62 ml (6 grams) of alcohol in Austria, but in Japan it is 25 ml (19.75 grams).
- In the United Kingdom, there is a system of units of alcohol which serves as a guideline for alcohol consumption. A single unit of alcohol is defined as 10 ml. The number of units present in a typical drink is sometimes printed on bottles. The system is intended as an aid to people who are regulating the amount of alcohol they drink; it is not used to determine serving sizes.
- In the United States, the standard drink contains 0.6 US fluid ounces (18 ml) of alcohol. This is approximately the amount of alcohol in a 12-US-fluid-ounce (350 ml) glass of beer, a 5-US-fluid-ounce (150 ml) glass of wine, or a 1.5-US-fluid-ounce (44 ml) glass of a 40% ABV (80 US proof) spirit.
Laws
Alcohol laws regulate the manufacture, packaging, labelling, distribution, sale, consumption, blood alcohol content of motor vehicle drivers, open containers, and transportation of alcoholic drinks. Such laws generally seek to reduce the adverse health and social impacts of alcohol consumption. In particular, alcohol laws set the legal drinking age, which usually varies between 16 and 25 years, sometimes depending upon the type of drink (e.g., beer vs. hard liquor). Some countries do not have a legal drinking or purchasing age, but most countries set the minimum age at 18 years.[2] Such laws may take the form of permitting distribution only to licensed stores, monopoly stores, or pubs and they are often combined with taxation, which serves to reduce the demand for alcohol (by raising its price) and it is a form of revenue for governments. These laws also often limit the hours or days (e.g., "blue laws") on which alcohol may be sold or served, as can also be seen in the "last call" ritual in US and Canadian bars, where bartenders and servers ask patrons to place their last orders for alcohol, due to serving hour cutoff laws. In some countries, alcohol cannot be sold to a person who is already intoxicated. Alcohol laws in many countries prohibit drunk driving.
In some jurisdictions, alcoholic drinks are totally prohibited for reasons of religion (e.g., Islamic countries with sharia law) or for reasons of local option, public health, and morals (e.g., Prohibition in the United States from 1920 to 1933). In jurisdictions which enforce sharia law, the consumption of alcoholic drinks is an illegal offense,[45] although such laws may exempt non-Muslims.[46]
History
- 10,000–5,000 BC: Discovery of late Stone Age jugs suggests that intentionally fermented drinks existed at least as early as the Neolithic period.[47]
- 7000–5600 BC: Examination and analysis of ancient pottery jars from the neolithic village of Jiahu in the Henan province of northern China revealed residue left behind by the alcoholic drinks they had once contained. According to a study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, chemical analysis of the residue confirmed that a fermented drink made of grape and hawthorn fruit wine, honey mead and rice beer was being produced in 7000–5600 BC (McGovern et al., 2005; McGovern 2009).[48][49] The results of this analysis were published in December 2004.[50]
- 9th century AD: The medieval Arabs used the distillation process extensively, and applied it to the distillation of alcohol. The Arab chemist Al-Kindi unambiguously described the distillation of wine in the 9th century.[51][52][53]
- 12th century: The process of distillation spread from the Middle East to Italy,[51][54] where distilled alcoholic drinks were recorded in the mid-12th century.[55] In China, archaeological evidence indicates that the true distillation of alcohol began during the 12th century Jin or Southern Song dynasties.[56] A still has been found at an archaeological site in Qinglong, Hebei, dating to the 12th century.[56]
- 14th century: In India, the true distillation of alcohol was introduced from the Middle East, and was in wide use in the Delhi Sultanate by the 14th century.[54] By the early 14th century, distilled alcoholic drinks had spread throughout the European continent.[55]
See also
- Beer and breweries by region
- Chinese alcoholic beverages
- Cooking with alcohol
- Homebrewing
- List of alcoholic drinks
- List of countries by alcohol consumption
- List of national drinks
- Mixed drink
Social and health
- Alcohol-related crime
- Alcohol and health
- Long-term effects of alcohol consumption
- Religion and alcohol
- Short-term effects of alcohol consumption
References
- ↑ "Worldwide Alcohol Consumption Declines -1.6% – IWSR". https://www.theiwsr.com/news-and-comment-worldwide-alcohol-consumption-declines/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Minimum Legal Age Limits". International Alliance for Responsible Drinking. http://www.iard.org/policy-tables/minimum-legal-age-limits/.
- ↑ "Worldwide Alcohol Consumption Declines -1.6%". International Wines and Spirits Record (ISWR). 2019-05-30. https://www.theiwsr.com/news-and-comment-worldwide-alcohol-consumption-declines/. Retrieved 2019-06-04.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Griswold, Max G.; Fullman, Nancy; Hawley, Caitlin; Arian, Nicholas; Zimsen, Stephanie R M.; Tymeson, Hayley D.; Venkateswaran, Vidhya; Tapp, Austin Douglas et al. (August 2018). "Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016". The Lancet 392 (10152): 1015–35. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2. PMID 30146330.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Alcohol Facts and Statistics". National Institute of Health. August 2018. http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/alcohol-facts-and-statistics. Retrieved 8 October 2018.
- ↑ Charles H, Patrick; Durham, NC (1952). Alcohol, Culture, and Society. Duke University Press (reprint edition by AMS Press, New York, 1970). pp. 26–27. ISBN 978-0-404-04906-5.
- ↑ Zielinski, Sarah (16 September 2011). "The Alcoholics of the Animal World". Smithsonian. http://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/the-alcoholics-of-the-animal-world-81007700/.
- ↑ John C. Super, "Alcoholic Beverages" in Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture, vol. 1, p. 45. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons 1996.
- ↑ Nelson, Max (2005). The Barbarian's Beverage: A History of Beer in Ancient Europe. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-415-31121-2. https://books.google.com/?id=6xul0O_SI1MC&pg=PA1&dq=most+consumed+beverage. Retrieved 21 September 2010.
- ↑ Martin Dworkin, Stanley Falkow (2006). The Prokaryotes: Proteobacteria: alpha and beta subclasses. Springer. p. 169. ISBN 978-0-387-25495-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=sTsC65kCJbUC&pg=PA169. Retrieved 29 July 2011.
- ↑ Super, "Alcoholic Beverages", pp. 45–46.
- ↑ "Distilled spirit/distilled liquor". Britannica.com. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9106006/distilled-spirit. Retrieved 2013-02-05.
- ↑ Lichine, Alexis. Alexis Lichine's New Encyclopedia of Wines & Spirits (5th edition) (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1987), 707–709.
- ↑ Lichine, Alexis (1987). Alexis Lichine's New Encyclopedia of Wines & Spirits (5th ed.). New York: Alfred A. Knopf. p. 236. ISBN 978-0-394-56262-9.
- ↑ Robinson, J., ed (2006). The Oxford Companion to Wine (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. p. 279. ISBN 978-0-19-860990-2. https://archive.org/details/oxfordcompaniont00janc/page/279.
- ↑ Roberts, C.; Robinson, S.P. (2007). "Alcohol concentration and carbonation of drinks: The effect on blood alcohol levels". Journal of Forensic and Legal Medicine 14 (7): 398–405. doi:10.1016/j.jflm.2006.12.010. PMID 17720590.
- ↑ Levine, Barry (2003). Principles of Forensic Toxicology. Amer. Assoc. for Clinical Chemistry. pp. 161–. ISBN 978-1-890883-87-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=k7BInEQ-iqgC&pg=PA161.
- ↑ Alcohol dissolves freely in the water of the human body. Thus, blood alcohol content and body water alcohol content are the same. A man contains 77% water, which is 770 dL, giving 12 g/h, or 15 ml/h.
- ↑ "Non-Alcoholic Red Wine May Boost Heart Health". http://www.webmd.com/hypertension-high-blood-pressure/news/20120906/nonalcoholic-red-wine-may-boost-heart-health. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 O'Keefe, JH; Bhatti, SK; Bajwa, A; DiNicolantonio, JJ; Lavie, CJ (March 2014). "Alcohol and cardiovascular health: the dose makes the poison...or the remedy.". Mayo Clinic Proceedings 89 (3): 382–93. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.11.005. PMID 24582196.
- ↑ Schuckit, MA (27 November 2014). "Recognition and management of withdrawal delirium (delirium tremens).". The New England Journal of Medicine 371 (22): 2109–13. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1407298. PMID 25427113. http://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/08b9z9th.
- ↑ Cheryl Platzman Weinstock (8 November 2017). "Alcohol Consumption Increases Risk of Breast and Other Cancers, Doctors Say". Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/alcohol-consumption-increases-risk-of-breast-and-other-cancers-doctors-say/. Retrieved 13 November 2018.
- ↑ Catherine Thorbecke (7 November 2017). "Even moderate alcohol consumption may increase risk of certain cancers, experts warn". ABC. https://abcnews.go.com/Health/moderate-alcohol-consumption-increase-risk-cancers-experts-warn/story?id=50996234. Retrieved 13 November 2018.
- ↑ Alcohol and Heart Health American Heart Association
- ↑ "Alcohol Use and Cancer". Cancer.org. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancercauses/dietandphysicalactivity/alcohol-use-and-cancer. Retrieved 2016-08-25.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "General Information on Alcohol Use and Health". https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol/quickstats/general_info.htm. Retrieved 26 June 2008.
- ↑ American Heart Association. "Alcohol, Wine and Cardiovascular Disease". http://www.americanheart.org/presenter.jhtml?identifier=4422. Retrieved 26 June 2008.
- ↑ Cogliano, VJ; Baan, R; Straif, K; Grosse, Y; Lauby-Secretan, B; El Ghissassi, F; Bouvard, V; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L et al. (December 21, 2011). "Preventable exposures associated with human cancers.". Journal of the National Cancer Institute 103 (24): 1827–39. doi:10.1093/jnci/djr483. PMID 22158127.
- ↑ Understanding Congeners in Wine, Wines & Vines. Accessed 2011-4-20
- ↑ Whisky hangover 'worse than vodka, a study suggests', BBC News. Accessed 2009-12-19
- ↑ "The 5 Basic Wine Characteristics". Wine Folly. 2012-07-23. http://winefolly.com/review/wine-characteristics/. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ↑ "Composition of Foods Raw, Processed, Prepared USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 26 Documentation and User Guide". USDA. August 2013. p. 14. http://www.ars.usda.gov/sp2UserFiles/Place/12354500/Data/SR26/sr26_doc.pdf.
- ↑ Robert Metz (1969). "Potentiation of the Plasma Insulin Response to Glucose by Prior Administration of Alcohol". Diabetes 18 (8): 517–22. doi:10.2337/diab.18.8.517. PMID 4897290. http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/18/8/517.full.pdf.
- ↑ Shelmet, JJ; Reichard, GA; Skutches, CL; Hoeldtke, RD; Owen, OE; Boden, G (1988). "Ethanol Causes Acute Inhibition of Carbohydrate, Fat, and Protein Oxidation and Insulin Resistance". J. Clin. Invest. 81 (4): 1137–45. doi:10.1172/JCI113428. PMID 3280601.
- ↑ Caton, S.J.; Ball, M; Ahern, A; Hetherington, M.M. (2004). "Dose-dependent effects of alcohol on appetite and food intake". Physiology & Behavior 81 (1): 51–58. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2003.12.017. PMID 15059684.
- ↑ Scinska, A; Koros, E; Habrat, B; Kukwa, A; Kostowski, W; Bienkowski, P (2000). "Bitter and sweet components of ethanol taste in humans". Drug and Alcohol Dependence 60 (2): 199–206. doi:10.1016/s0376-8716(99)00149-0. PMID 10940547.
- ↑ "6 Secrets of Cooking with Wine". http://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/features/6-secrets-of-cooking-with-wine#1.
- ↑ Parker, Robert M. (2008). Parker's Wine Buyer's Guide, 7th Edition. Simon and Schuster. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-4391-3997-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=bHp1GJk8IMcC&pg=PA15.
- ↑ Jancis Robinson (2006). The Oxford Companion to Wine (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. https://archive.org/details/oxfordcompaniont00janc. See alcoholic strength at p. 10.
- ↑ "Find the Alcohol Contents of Beer, Wine, and Liquor". http://www.alcoholcontents.com/. Retrieved 6 May 2015.
- ↑ Lichine, Alexis. Alexis Lichine's New Encyclopedia of Wines & Spirits (5th edition) (New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1987), 365.
- ↑ Stewart, Graham G. "Biographical Review: Seduced by Yeast". Journal of the American Society of Brewing Chemists (2015): 1–21. American Society of Brewing Chemists. 21 Jan. 2015. Web. 14 May 2017.
- ↑ "fifedirect – Licensing & Regulations – Calling Time on Short Measures!". Fifefire.gov.uk. 2008-07-29. Archived from the original on 2011-07-22. https://web.archive.org/web/20110722175012/http://www.fifefire.gov.uk/topics/index.cfm?fuseaction=news.display&subjectid=8133D50D-A872-4A5B-9C65EE07BBF04E7E&objectid=6DDC0AD4-C85A-2F07-BE70B5A0D64D0A58. Retrieved 2010-02-11.
- ↑ Wansink, Brian; van Ittersum, Koert (2005). "Shape of glass and amount of alcohol poured: comparative study of effect of practice and concentration". BMJ 331 (7531): 1512–14. doi:10.1136/bmj.331.7531.1512. PMID 16373735. PMC 1322248. http://www.bmj.com/content/331/7531/1512.
- ↑ Williams, Lizzie. Nigeria: The Bradt Travel Guide. p. 101.
- ↑ Alcohol and Temperance in Modern History p. 329 David M. Fahey, Ian R. Tyrrell (2003)
- ↑ Patrick, Clarence Hodges (1952). Alcohol, Culture, and Society. Durham, NC: Duke University Press (reprint edition by AMS Press, New York, 1970). pp. 26–27. ISBN 978-0-404-04906-5.
- ↑ Chrzan, Janet (2013). Alcohol: Social Drinking in Cultural Context. Routledge. p. 13. ISBN 978-0-415-89249-0.
- ↑ McGovern, P.E.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hall, G.R.; Moreau, R.A.; Nunez, A.; Butrym, E.D. et al. (2004). "Fermented beverages of pre- and proto-historic China". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 101 (51): 17593–98. doi:10.1073/pnas.0407921102. PMID 15590771. Bibcode: 2004PNAS..10117593M.
- ↑ Roach, John. "Cheers! Eight ancient drinks uncorked by science". Nbc News. http://www.nbcnews.com/id/34435526/ns/technology_and_science-science/t/cheers-eight-ancient-drinks-uncorked-science/. Retrieved 9 June 2013.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 Ahmad Y. al-Hassan (2001), Science and Technology in Islam: Technology and applied sciences, pp. 65-69, UNESCO
- ↑ Hassan, Ahmad Y. "Alcohol and the Distillation of Wine in Arabic Sources". History of Science and Technology in Islam. http://www.history-science-technology.com/notes/notes7.html. Retrieved 2014-04-19.
- ↑ The Economist: "Liquid fire – The Arabs discovered how to distill alcohol. They still do it best, say some" December 18, 2003
- ↑ 54.0 54.1 Irfan Habib (2011), Economic History of Medieval India, 1200–1500, p. 55, Pearson Education
- ↑ 55.0 55.1 Forbes, Robert James (1970). A Short History of the Art of Distillation: From the Beginnings up to the Death of Cellier Blumenthal. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-00617-1. https://books.google.com/?id=XeqWOkKYn28C. Retrieved 28 June 2010.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 Haw, Stephen G. (2006). "Wine, women and poison". Marco Polo in China. Routledge. pp. 147–48. ISBN 978-1-134-27542-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=DSfvfr8VQSEC&pg=PA148. Retrieved 2016-07-10. "The earliest possible period seems to be the Eastern Han dynasty... the most likely period for the beginning of true distillation of spirits for drinking in China is during the Jin and Southern Song dynasties"
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Alcoholic beverages. |
- About 37 percent of college students could now be considered alcoholics, Daily Emerald
- Alcohol, Health-EU Portal, Health-EU Portal
- What Is a Standard Drink?, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism