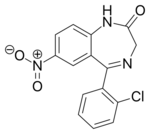
Chemistry:Clonazepam
| |||
| Clinical data | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | kləˈnazɪpam | ||
| Trade names | Klonopin, Rivotril, Paxam,[1] others[2] | ||
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph | ||
| MedlinePlus | a682279 | ||
| License data |
| ||
| Pregnancy category |
| ||
| Dependence liability | Physical: Very High | ||
| Addiction liability | Moderate[4][5] | ||
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intramuscular, intravenous, sublingual | ||
| Drug class | Benzodiazepine | ||
| ATC code | |||
| Legal status | |||
| Legal status |
| ||
| Pharmacokinetic data | |||
| Bioavailability | 90% | ||
| Protein binding | ≈85% | ||
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A)[10] | ||
| Metabolites | 7-aminoclonazepam 7-acetaminoclonazepam 3-hydroxy clonazepam[6][7] | ||
| Onset of action | Within an hour[8] | ||
| Elimination half-life | 19–60 hours[9] | ||
| Duration of action | 6–12 hours[8] | ||
| Excretion | Kidney | ||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
| CAS Number | |||
| PubChem CID | |||
| IUPHAR/BPS | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| UNII | |||
| KEGG | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| Chemical and physical data | |||
| Formula | C15H10ClN3O3 | ||
| Molar mass | 315.71 g·mol−1 | ||
| 3D model (JSmol) | |||
| |||
| |||
| (verify) | |||
Clonazepam, sold under the brand names Klonopin and Rivotril, is a medication used to prevent and treat anxiety disorders, seizures, bipolar mania, agitation associated with psychosis, OCD and akathisia.[10] It is a tranquilizer of the benzodiazepine class.[10] It possesses anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, sedative, hypnotic, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. It is typically taken by mouth but is also used intravenously.[10][11] Effects begin within one hour and last between six and twelve hours.[8]
Common side effects may include sleepiness, poor coordination, and agitation.[10] Long-term use may result in tolerance, dependence, and life-threatening withdrawal symptoms if stopped abruptly.[10][12] Dependence occurs in one-third of people who take benzodiazepines for longer than four weeks.[9] The risk of suicide increases, particularly in people who are already depressed.[10][13] Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the fetus.[10] Clonazepam binds to GABAA receptors, thus increasing the effect of the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA).[9]
Clonazepam was patented in 1960 and went on sale in 1975 in the United States from Roche.[14][15] It is available as a generic medication.[10] In 2021, it was the 46th-most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 14 million prescriptions.[16][17] In many areas of the world, it is commonly used as a recreational drug.[18][19]
Medical uses
Clonazepam is prescribed for short-term management of epilepsy, anxiety, OCD and panic disorder with or without agoraphobia.[20][21][22]
Seizures
Clonazepam, like other benzodiazepines, while being a first-line treatment for acute seizures, is not suitable for the long-term treatment of seizures due to the development of tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects.
Clonazepam has been found effective in treating epilepsy in children, and the inhibition of seizure activity seemed to be achieved at low plasma levels of clonazepam.[23] As a result, clonazepam is sometimes used for certain rare childhood epilepsies, but it has been found to be ineffective in the control of infantile spasms.[24] Clonazepam is mainly prescribed for the acute management of epilepsies. Clonazepam has been found to be effective in the acute control of nonconvulsive status epilepticus; the benefits, though, tended to be transient in many people, and the addition of phenytoin for lasting control was required in these patients.[25]
It is also approved for treatment of typical and atypical absences (seizures), infantile myoclonic, myoclonic, and akinetic seizures.[26] A subgroup of people with treatment resistant epilepsy may benefit from long-term use of clonazepam; the benzodiazepine clorazepate may be an alternative due to its slow onset of tolerance.[9][27]
Anxiety disorders
- Panic disorder may occur with or without agoraphobia.[28]
- Clonazepam has also been found effective in treating other anxiety disorders, such as social phobia, but this is an off-label use.[29][30]
The effectiveness of clonazepam in the short-term treatment of panic disorder has been demonstrated in controlled clinical trials. Some long-term trials have suggested a benefit of clonazepam for up to three years without the development of tolerance.[31] Clonazepam is also effective in the management of acute mania.[32]
Muscle disorders
Restless legs syndrome can be treated using clonazepam as a third-line treatment option, as the use of clonazepam is still investigational.[33][34] Bruxism also responds to clonazepam in the short term.[35] REM sleep behavior disorder responds well to low doses of clonazepam.[36] It is also used for:
- The treatment of acute and chronic akathisia induced by neuroleptics, also called antipsychotics[37][38]
- Spasticity related to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[39]
Other
- Benzodiazepines, such as clonazepam, are sometimes used for the treatment of mania or acute psychosis-induced aggression. In this context, benzodiazepines are given either alone or in combination with other first-line drugs such as lithium, haloperidol, or risperidone.[40][41] The effectiveness of taking benzodiazepines along with antipsychotic medication is unknown, and more research is needed to determine if benzodiazepines are more effective than antipsychotics when urgent sedation is required.[41]
- Hyperekplexia[42]
- Many forms of parasomnia and other sleep disorders are treated with clonazepam.[43]
- It is not effective for preventing migraines.[44]
Contraindications
- Coma
- Current alcohol use disorder
- Current substance use disorder
- Respiratory depression[45]
Adverse effects
In September 2020, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration required the boxed warning be updated for all benzodiazepine medicines to describe the risks of abuse, misuse, addiction, physical dependence, and withdrawal reactions consistently across all the medicines in the class.[46]
Common
Less common
- Confusion[9]
- Irritability and aggression[48]
- Psychomotor agitation[49]
- Lack of motivation[50]
- Loss of libido
- Impaired motor function
- Impaired coordination
- Impaired balance
- Dizziness
- Cognitive impairments[vague][51]
- Hallucinations.[52]
- Short-term memory loss[53]
- Anterograde amnesia (common with higher doses)[54]
- Some users report hangover-like symptoms of drowsiness, headaches, sluggishness, and irritability upon waking up if the medication was taken before sleep. This is likely the result of the medication's long half-life, which continues to affect the user after waking up.[55][56][57] While benzodiazepines induce sleep, they tend to reduce the quality of sleep by suppressing or disrupting REM sleep.[58] After regular use, rebound insomnia may occur when discontinuing clonazepam.[59]
- Benzodiazepines may cause or worsen depression.[9]
Occasional
- Dysphoria[60]
- Induction of seizures[61][62] or increased frequency of seizures[63]
- Personality changes[64]
- Behavioural disturbances[65]
- Ataxia[9]
Rare
- Suicide through disinhibition[13]
- Psychosis[66]
- Incontinence[67][68][69]
- Paradoxical behavioural disinhibition[9][70] (most frequently in children, the elderly, and in persons with developmental disabilities)
- Rage
- Excitement
- Impulsivity
The long-term effects of clonazepam can include depression,[9] disinhibition, and sexual dysfunction.[71]
Drowsiness
Clonazepam, like other benzodiazepines, may impair a person's ability to drive or operate machinery. The central nervous system depressing effects of the drug can be intensified by alcohol consumption, so alcohol should be avoided while taking this medication. Benzodiazepines have been shown to cause dependence. Patients dependent on clonazepam should be slowly titrated off under the supervision of a qualified healthcare professional to reduce the intensity of withdrawal or rebound symptoms.
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Insomnia
- Tremors
- Headaches
- Stomach pain
- Hallucinations
- Suicidal thoughts or urges
- Depression
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Potential to exacerbate existing panic disorder upon discontinuation
- Seizures[72] similar to delirium tremens (with long-term use of excessive doses)
Benzodiazepines such as clonazepam can be very effective in controlling status epilepticus, but, when used for longer periods of time, some potentially serious side-effects may develop, such as interference with cognitive functions and behavior.[73] Many individuals treated on a long-term basis develop a dependence. Physiological dependence was demonstrated by flumazenil-precipitated withdrawal.[74] Use of alcohol or other CNS depressants while taking clonazepam greatly intensifies the effects (and side effects) of the drug.
A recurrence of symptoms of the underlying disease should be separated from withdrawal symptoms.[75]
Tolerance and withdrawal
Like all benzodiazepines, clonazepam is a GABA-positive allosteric modulator.[76][77] One-third of individuals treated with benzodiazepines for longer than four weeks develop a dependence on the drug and experience a withdrawal syndrome upon dose reduction. High dosage and long-term use increase the risk and severity of dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Withdrawal seizures and psychosis can occur in severe cases of withdrawal, and anxiety and insomnia can occur in less severe cases of withdrawal. A gradual reduction in dosage reduces the severity of the benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome. Due to the risks of tolerance and withdrawal seizures, clonazepam is generally not recommended for the long-term management of epilepsies. Increasing the dose can overcome the effects of tolerance, but tolerance to the higher dose may occur and adverse effects may intensify. The mechanism of tolerance includes receptor desensitization, down regulation, receptor decoupling, and alterations in subunit composition and in gene transcription coding.[9]
Tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects of clonazepam occurs in both animals and humans. In humans, tolerance to the anticonvulsant effects of clonazepam occurs frequently.[78][79] Chronic use of benzodiazepines can lead to the development of tolerance with a decrease of benzodiazepine binding sites. The degree of tolerance is more pronounced with clonazepam than with chlordiazepoxide.[80] In general, short-term therapy is more effective than long-term therapy with clonazepam for the treatment of epilepsy.[81] Many studies have found that tolerance develops to the anticonvulsant properties of clonazepam with chronic use, which limits its long-term effectiveness as an anticonvulsant.[26]
Abrupt or over-rapid withdrawal from clonazepam may result in the development of the benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome, causing psychosis characterised by dysphoric manifestations, irritability, aggressiveness, anxiety, and hallucinations.[82][83][84] Sudden withdrawal may also induce the potentially life-threatening condition, status epilepticus. Anti-epileptic drugs, benzodiazepines such as clonazepam in particular, should be reduced in dose slowly and gradually when discontinuing the drug to mitigate withdrawal effects.[64] Carbamazepine has been tested in the treatment of clonazepam withdrawal but was found to be ineffective in preventing clonazepam withdrawal-induced status epilepticus from occurring.[85]
Overdose
Excess doses may result in:
- Difficulty staying awake
- Mental confusion
- Impaired motor functions
- Impaired reflexes
- Impaired coordination
- Impaired balance
- Dizziness
- Respiratory depression
- Low blood pressure
- Coma
Coma can be cyclic, with the individual alternating from a comatose state to a hyper-alert state of consciousness, which occurred in a four-year-old boy who overdosed on clonazepam.[86] The combination of clonazepam and certain barbiturates (for example, amobarbital), at prescribed doses has resulted in a synergistic potentiation of the effects of each drug, leading to serious respiratory depression.[87]
Overdose symptoms may include extreme drowsiness, confusion, muscle weakness, and fainting.[88]
Detection in biological fluids
Clonazepam and 7-aminoclonazepam may be quantified in plasma, serum, or whole blood in order to monitor compliance in those receiving the drug therapeutically. Results from such tests can be used to confirm the diagnosis in potential poisoning victims or to assist in the forensic investigation in a case of fatal overdosage. Both the parent drug and 7-aminoclonazepam are unstable in biofluids, and therefore specimens should be preserved with sodium fluoride, stored at the lowest possible temperature and analyzed quickly to minimize losses.[89]
Special precautions
The elderly metabolize benzodiazepines more slowly than younger people and are also more sensitive to the effects of benzodiazepines, even at similar blood plasma levels. Doses for the elderly are recommended to be about half of that given to younger adults and are to be administered for no longer than two weeks. Long-acting benzodiazepines such as clonazepam are not generally recommended for the elderly due to the risk of drug accumulation.[9]
The elderly are especially susceptible to increased risk of harm from motor impairments and drug accumulation side effects. Benzodiazepines also require special precaution if used by individuals that may be pregnant, alcohol- or drug-dependent, or may have comorbid psychiatric disorders.[90] Clonazepam is generally not recommended for use in elderly people for insomnia due to its high potency relative to other benzodiazepines.[91]
Clonazepam is not recommended for use in those under 18. Use in very young children may be especially hazardous. Of anticonvulsant drugs, behavioural disturbances occur most frequently with clonazepam and phenobarbital.[90][92]
Doses higher than 0.5–1 mg per day are associated with significant sedation.[93]
Clonazepam may aggravate hepatic porphyria.[94][95]
Clonazepam is not recommended for patients with chronic schizophrenia. A 1982 double-blinded, placebo-controlled study found clonazepam increases violent behavior in individuals with chronic schizophrenia.[96]
Clonazepam has similar effectiveness to other benzodiazepines at often a lower dose.[97]
Interactions
Clonazepam decreases the levels of carbamazepine,[98][99] and, likewise, clonazepam's level is reduced by carbamazepine. Azole antifungals, such as ketoconazole, may inhibit the metabolism of clonazepam.[9] Clonazepam may affect levels of phenytoin (diphenylhydantoin).[98][100][101][102] In turn, Phenytoin may lower clonazepam plasma levels by increasing the speed of clonazepam clearance by approximately 50% and decreasing its half-life by 31%.[103] Clonazepam increases the levels of primidone[101] and phenobarbital.[104]
Combined use of clonazepam with certain antidepressants, anticonvulsants (such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine), sedative antihistamines, opiates, and antipsychotics, nonbenzodiazepines (such as zolpidem), and alcohol may result in enhanced sedative effects.[9]
Pregnancy
There is some medical evidence of various malformations (for example, cardiac or facial deformations when used in early pregnancy); however, the data is not conclusive. The data are also inconclusive on whether benzodiazepines such as clonazepam cause developmental deficits or decreases in IQ in the developing fetus when taken by the mother during pregnancy. Clonazepam, when used late in pregnancy, may result in the development of a severe benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome in the neonate. Withdrawal symptoms from benzodiazepines in the neonate may include hypotonia, apnoeic spells, cyanosis, and impaired metabolic responses to cold stress.[105]
The safety profile of clonazepam during pregnancy is less clear than that of other benzodiazepines, and if benzodiazepines are indicated during pregnancy, chlordiazepoxide and diazepam may be a safer choice. The use of clonazepam during pregnancy should only occur if the clinical benefits are believed to outweigh the clinical risks to the fetus. Caution is also required if clonazepam is used during breastfeeding. Possible adverse effects of use of benzodiazepines such as clonazepam during pregnancy include: miscarriage, malformation, intrauterine growth retardation, functional deficits, carcinogenesis, and mutagenesis. Neonatal withdrawal syndrome associated with benzodiazepines include hypertonia, hyperreflexia, restlessness, irritability, abnormal sleep patterns, inconsolable crying, tremors, or jerking of the extremities, bradycardia, cyanosis, suckling difficulties, apnea, risk of aspiration of feeds, diarrhea and vomiting, and growth retardation. This syndrome can develop between three days to three weeks after birth and can have a duration of up to several months. The pathway by which clonazepam is metabolized is usually impaired in newborns. If clonazepam is used during pregnancy or breastfeeding, it is recommended that serum levels of clonazepam are monitored and that signs of central nervous system depression and apnea are also checked for. In many cases, non-pharmacological treatments, such as relaxation therapy, psychotherapy, and avoidance of caffeine, can be an effective and safer alternative to the use of benzodiazepines for anxiety in pregnant women.[106]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Clonazepam enhances the activity of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the central nervous system to give its anticonvulsant, skeletal muscle relaxant, and anxiolytic effects.[107] It acts by binding to the benzodiazepine site of the GABA receptors, which enhances the electric effect of GABA binding on neurons, resulting in an increased influx of chloride ions into the neurons. This further results in an inhibition of synaptic transmission across the central nervous system.[108][109]
Benzodiazepines do not have any effect on the levels of GABA in the brain.[110] Clonazepam has no effect on GABA levels and has no effect on gamma-aminobutyric acid transaminase. Clonazepam does, however, affect glutamate decarboxylase activity. It differs from other anticonvulsant drugs it was compared to in a study.[111]
Clonazepam's primary mechanism of action is the modulation of GABA function in the brain, by the benzodiazepine receptor, located on GABAA receptors, which, in turn, leads to enhanced GABAergic inhibition of neuronal firing. Benzodiazepines do not replace GABA, but instead enhance the effect of GABA at the GABAA receptor by increasing the opening frequency of chloride ion channels, which leads to an increase in GABA's inhibitory effects and resultant central nervous system depression.[9] In addition, clonazepam decreases the utilization of 5-HT (serotonin) by neurons[112][113] and has been shown to bind tightly to central-type benzodiazepine receptors.[114] Because clonazepam is effective in low milligram doses (0.5 mg clonazepam = 10 mg diazepam),[115][116] it is said to be among the class of "highly potent" benzodiazepines.[117] The anticonvulsant properties of benzodiazepines are due to the enhancement of synaptic GABA responses, and the inhibition of sustained, high-frequency repetitive firing.[118]
Benzodiazepines, including clonazepam, bind to mouse glial cell membranes with high affinity.[119][120] Clonazepam decreases release of acetylcholine in the feline brain[121] and decreases prolactin release in rats.[122] Benzodiazepines inhibit cold-induced thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as TSH or thyrotropin) release.[123] Benzodiazepines act via micromolar benzodiazepine binding sites as Ca2+ channel blockers and significantly inhibit depolarization-sensitive calcium uptake in experimentation on rat brain cell components. This has been conjectured as a mechanism for high-dose effects on seizures in the study.[124]
Clonazepam is a 2'-chlorinated derivative of nitrazepam, which increases its potency due to electron-attracting effect of the halogen in the ortho-position.[125][8]
Pharmacokinetics
Clonazepam is lipid-soluble, rapidly crosses the blood–brain barrier, and penetrates the placenta. It is extensively metabolised into pharmacologically inactive metabolites, with only 2% of the unchanged drug excreted in the urine.[126] Clonazepam is metabolized extensively via nitroreduction by cytochrome P450 enzymes, including CYP3A4. Erythromycin, clarithromycin, ritonavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, cimetidine, and grapefruit juice are inhibitors of CYP3A4 and can affect the metabolism of benzodiazepines.[127] It has an elimination half-life of 19–60 hours.[9] Peak blood concentrations of 6.5–13.5 ng/mL were usually reached within 1–2 hours following a single 2 mg oral dose of micronized clonazepam in healthy adults. In some individuals, however, peak blood concentrations were reached at 4–8 hours.[128]
Clonazepam passes rapidly into the central nervous system, with levels in the brain corresponding with levels of unbound clonazepam in the blood serum.[129] Clonazepam plasma levels are very unreliable amongst patients. Plasma levels of clonazepam can vary as much as tenfold between different patients.[130]
Clonazepam has plasma protein binding of 85%.[131][126] Clonazepam passes through the blood–brain barrier easily, with blood and brain levels corresponding equally with each other.[132] The metabolites of clonazepam include 7-aminoclonazepam, 7-acetaminoclonazepam and 3-hydroxy clonazepam.[6][133] These metabolites are excreted by the kidney.[126]
It is effective for 6–8 hours in children, and 6–12 in adults.[134]
Society and culture
Recreational use
A 2006 US government study of hospital emergency department (ED) visits found that sedative-hypnotics were the most frequently implicated pharmaceutical drug in visits, with benzodiazepines accounting for the majority of these. Clonazepam was the second most frequently implicated benzodiazepine in ED visits. Alcohol alone was responsible for over twice as many ED visits as clonazepam in the same study. The study examined the number of times the non-medical use of certain drugs was implicated in an ED visit. The criteria for non-medical use in this study were purposefully broad, and include, for example, drug abuse, accidental or intentional overdose, or adverse reactions resulting from legitimate use of the medication.[135]
Formulations
Clonazepam was approved in the United States as a generic drug in 1997 and is now manufactured and marketed by several companies.
Clonazepam is available as tablets and orally disintegrating tablets (wafers) an oral solution (drops), and as a solution for injection or intravenous infusion.[136]
Crime
In some countries, clonazepam is used by criminals to subdue their victims.[137]
Brand names
It is marketed under the trade name Rivotril by Roche in Argentina, Australia, Austria, Bangladesh, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Colombia, Costa Rica, Croatia, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia,[138] Germany, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, China, Mexico, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, Peru, Pakistan, Romania, Serbia, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Turkey, and the United States; Emcloz, Linotril, Lonazep, Clotrin and Clonotril in India and other parts of Europe; under the name Riklona in Indonesia and Malaysia; and under the trade name Klonopin by Roche in the United States. Other names, such as Antelepsin, Clonoten, Ravotril, Rivotril, Iktorivil, Clonex (Israel), Paxam, Petril, Naze, Zilepam and Kriadex, are used throughout the world.[2][136] In August 2021, Roche Australia transferred Rivotril to Pharmaco Australia Ltd.[139]
References
- ↑ https://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/datasheet/p/Paxamtab.pdf
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Clonazepam International". Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/international/clonazepam.html.
- ↑ "Clonazepam Use During Pregnancy". 4 May 2020. https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/clonazepam.html.
- ↑ "Addiction: Part I. Benzodiazepines--side effects, abuse risk and alternatives". American Family Physician 61 (7): 2121–2128. April 2000. PMID 10779253. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2000/0401/p2121.html.
- ↑ Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery - E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2013. p. 679. ISBN 9780323226875. https://books.google.com/books?id=RcbsAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA679.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "[Studies on the detection of clonazepam and its main metabolites considering in particular thin-layer chromatography discrimination of nitrazepam and its major metabolic products (author's transl)]". Arzneimittel-Forschung 27 (2): 325–337. February 1977. PMID 577149.
- ↑ "Blood concentrations of clonazepam and 7-aminoclonazepam in forensic cases in Denmark for the period 2002-2007". Forensic Science International 184 (1–3): 74–79. January 2009. doi:10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.12.004. PMID 19150586.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Therapeutic uses of botulinum toxin. Totowa, N.J.: Humana Press. 2007. p. 214. ISBN 9781597452472. https://books.google.com/books?id=UIUhCmMtqq8C&pg=PA214.
- ↑ 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 "Benzodiazepines in epilepsy: pharmacology and pharmacokinetics". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 118 (2): 69–86. August 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2008.01004.x. PMID 18384456.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.7 10.8 "Clonazepam". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. https://www.drugs.com/monograph/clonazepam.html.
- ↑ "Intravenous Clonazepam in Status Epilepticus". Epilepsy Currents 16 (2): 89–90. 2016. doi:10.5698/1535-7511-16.2.89. PMID 27073337.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepines: Uses, Dangers, and Clinical Considerations". Neurology International 13 (4): 594–607. November 2021. doi:10.3390/neurolint13040059. PMID 34842811.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Prescribed Benzodiazepines and Suicide Risk: A Review of the Literature". The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders 19 (2). March 2017. doi:10.4088/PCC.16r02037. PMID 28257172.
- ↑ Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. 2006. p. 535. ISBN 9783527607495. https://books.google.com/books?id=FjKfqkaKkAAC&pg=PA535.
- ↑ "B". A Historical Dictionary of Psychiatry. Oxford University Press. 2005. ISBN 9780190292010. https://books.google.com/books?id=juAJCAAAQBAJ&pg=PT66.
- ↑ "The Top 300 of 2021". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Top300Drugs.aspx.
- ↑ "Clonazepam - Drug Usage Statistics". https://clincalc.com/DrugStats/Drugs/Clonazepam.
- ↑ Advances in the neurochemistry and neuropharmacology of Tourette Syndrome. Burlington: Elsevier Science. 2013. p. 357. ISBN 9780124115613. https://books.google.com/books?id=RYhqAAAAQBAJ&pg=PA357. "In several countries, prescription and use is now severely limited due to abusive recreational use of clonazepam."
- ↑ Encyclopedia of substance abuse prevention, treatment, & recovery. Los Angeles: SAGE. 2009. p. 100. ISBN 9781412950848. https://books.google.com/books?id=CGxXIspuXVMC&pg=PT134. "frequently abused"
- ↑ "Propofol treatment of refractory status epilepticus: a study of 31 episodes". Epilepsia 45 (7): 757–763. July 2004. doi:10.1111/j.0013-9580.2004.01904.x. PMID 15230698.
- ↑ "Kinetics of clonazepam in relation to electroencephalographic and clinical effects". Epilepsia 24 (2): 225–231. April 1983. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1983.tb04883.x. PMID 6403345.
- ↑ "Clonazepam: medicine to control seizures or fits, muscle spasms and restless legs syndrome" (in en). 6 January 2020. https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/clonazepam/.
- ↑ "Reduction of seizures with low-dose clonazepam in children with epilepsy". Pediatric Neurology 28 (1): 48–52. January 2003. doi:10.1016/S0887-8994(02)00468-X. PMID 12657420.
- ↑ "Double-blind study of ACTH vs prednisone therapy in infantile spasms". The Journal of Pediatrics 103 (4): 641–645. October 1983. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(83)80606-4. PMID 6312008.
- ↑ "Nonconvulsive status epilepticus: high incidence of complex partial status". Epilepsia 27 (3): 276–285. May–Jun 1986. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1986.tb03540.x. PMID 3698940.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Clonazepam. A review of a new anticonvulsant drug". Archives of Neurology 33 (5): 326–332. May 1976. doi:10.1001/archneur.1976.00500050012003. PMID 817697.
- ↑ "Clonazepam add-on therapy for drug-resistant epilepsy". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (4): CD012253. April 2020. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD012253.pub3. PMID 32309880.
- ↑ "The treatment of panic disorder". Current Opinion in Psychiatry 18 (1): 45–50. January 2005. PMID 16639183. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/497207. Retrieved 25 September 2007.
- ↑ "Treatment of social phobia with clonazepam and placebo". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 13 (6): 423–428. December 1993. doi:10.1097/00004714-199312000-00008. PMID 8120156.
- ↑ (in en) A Practitioner's Guide to Prescribing Antiepileptics and Mood Stabilizers for Adults with Intellectual Disabilities. Springer Science & Business Media. 2 March 2012. ISBN 978-1-4614-2012-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=_LOzIqD3_NoC&q=Clonazepam+panic+approved&pg=PA56.
- ↑ "A randomized, naturalistic, parallel-group study for the long-term treatment of panic disorder with clonazepam or paroxetine". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 32 (1): 120–126. February 2012. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e31823fe4bd. PMID 22198456.
- ↑ "Clonazepam in the treatment of psychiatric disorders: an update". International Clinical Psychopharmacology 21 (3): 131–142. May 2006. doi:10.1097/01.yic.0000194379.65460.a6. PMID 16528135.
- ↑ "[Restless legs syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. Opinion of Brazilian experts]" (in Portuguese). Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria 65 (3A): 721–727. September 2007. doi:10.1590/S0004-282X2007000400035. PMID 17876423.
- ↑ "Treatment of restless legs syndrome: an evidence-based review and implications for clinical practice". Movement Disorders 23 (16): 2267–2302. December 2008. doi:10.1002/mds.22254. PMID 18925578. http://www.movementdisorders.org/publications/ebm_reviews/treatmentofrls.pdf. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- ↑ "Comparison of various treatments for sleep bruxism using determinants of number needed to treat and effect size". The International Journal of Prosthodontics 19 (5): 435–441. 2006. PMID 17323720.
- ↑ "REM sleep behavior disorder". Clinical Neurophysiology 111 (Suppl 2): S136–S140. September 2000. doi:10.1016/S1388-2457(00)00414-4. PMID 10996567.
- ↑ "Akathisia--a brief review". Scottish Medical Journal 46 (5): 133–134. October 2001. doi:10.1177/003693300104600502. PMID 11771491. http://smj.org.uk/1001/aka1001.htm. Retrieved 1 March 2009.
- ↑ "Successful treatment with clonazepam for neuroleptic-induced akathisia". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 80 (1): 106–107. July 1989. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.1989.tb01308.x. PMID 2569804.
- ↑ "Excitatory amino acids as a final common pathway for neurologic disorders". The New England Journal of Medicine 330 (9): 613–622. March 1994. doi:10.1056/NEJM199403033300907. PMID 7905600.
- ↑ "Clonazepam and lorazepam in acute mania: a Bayesian meta-analysis". Journal of Affective Disorders 78 (3): 201–208. March 2004. doi:10.1016/S0165-0327(02)00317-8. PMID 15013244.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 "Benzodiazepines for psychosis-induced aggression or agitation". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 4 (4): CD003079. April 2013. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003079.pub3. PMID 23633309.
- ↑ "Hyperekplexia: a treatable neurogenetic disease". Brain & Development 24 (7): 669–674. October 2002. doi:10.1016/S0387-7604(02)00095-5. PMID 12427512.
- ↑ "Sleep and sex: what can go wrong? A review of the literature on sleep related disorders and abnormal sexual behaviors and experiences". Sleep 30 (6): 683–702. June 2007. doi:10.1093/sleep/30.6.683. PMID 17580590.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsants in migraine prophylaxis: a Cochrane review". Cephalalgia 28 (6): 585–597. June 2008. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01571.x. PMID 18454787.
- ↑ Joint Formulary Committee. "British National Formulary (online)". London: BMJ Group and Pharmaceutical Press. http://www.medicinescomplete.com.
- ↑ "FDA expands Boxed Warning to improve safe use of benzodiazepine drug". 23 September 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requiring-boxed-warning-updated-improve-safe-use-benzodiazepine-drug-class.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ↑ "Sleep disorders in Parkinson's disease: epidemiology and management". Drugs & Aging 19 (10): 733–739. 2002. doi:10.2165/00002512-200219100-00002. PMID 12390050.
- ↑ "Some aspects of the clinical use of clonazepam in refractory epilepsy". Clinical and Experimental Neurology 16: 325–332. 1979. PMID 121707.
- ↑ "Comparative trial of intravenous lorazepam and clonazepam im status epilepticus". Clinical Therapeutics 4 (4): 326–336. 1981. PMID 6120763.
- ↑ "A hypernychthemeral sleep-wake syndrome: a treatment attempt". Chronobiology International 2 (4): 277–280. 1985. doi:10.3109/07420528509055890. PMID 3870855.
- ↑ Meyler's Side Effects of Psychiatric Drugs (Meylers Side Effects). Elsevier Science. 20 November 2008. p. 403. ISBN 978-0-444-53266-4.
- ↑ "Clonazepam Side Effects". Drugs.com. 2010. https://www.drugs.com/sfx/clonazepam-side-effects.html.
- ↑ The interface of neurology internal medicine. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams Wilkins. 1 September 2007. pp. 963. ISBN 978-0-7817-7906-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=SRIvmTVcYBwC&pg=RA2-PA963.
- ↑ The American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology (Schatzberg, American Psychiatric Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology). USA: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.. 31 July 2009. p. 471. ISBN 978-1-58562-309-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=Xx7iNGdV25IC&pg=PA471.
- ↑ "Get Some Sleep: Beware the sleeping pill hangover". http://thechart.blogs.cnn.com/2011/06/07/beware-the-sleeping-pill-hangover/.
- ↑ Narcolepsy:: A Clinical Guide. Springer. 24 March 2010. p. 73. ISBN 978-1-4419-0853-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=GvlZRKF_IA8C&pg=PA73.
- ↑ Principles of psychopharmacology for mental health professionals. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Liss. 2006. p. 269. ISBN 978-0-471-25401-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=FxaBz-ufvN0C&pg=PA269.
- ↑ Sleep Medicine: Essentials and Review. Oxford University Press, USA. 24 April 2008. pp. 463–465. ISBN 978-0-19-530659-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=2gzxPOBzZgUC&pg=PA463.
- ↑ Katzung Trevor's pharmacology: examination board review. New York: McGraw Hill Medical. 1 January 2008. p. 191. ISBN 978-0-07-148869-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=Bvtkl3XUC5AC&pg=PA191.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics and side-effects of clonazepam and its 7-amino-metabolite in man". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 8 (3–4): 249–254. April 1975. doi:10.1007/BF00567123. PMID 1233220.
- ↑ "Epileptic seizures induced by clonazepam". Clinical EEG 12 (2): 57–65. April 1981. doi:10.1177/155005948101200203. PMID 7237847.
- ↑ "[Multiple types of seizure induced by clonazepam in an epileptic patient]" (in ja). No to Hattatsu = Brain and Development 20 (4): 337–339. July 1988. PMID 3214607.
- ↑ "Clonazepam in the treatment of epilepsy. A clinical long-term follow-up study". Epilepsia 17 (3): 321–324. September 1976. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1976.tb03410.x. PMID 824124.
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 "Recent advances in drug therapy for epilepsy". Canadian Medical Association Journal 120 (7): 817–824. April 1979. PMID 371777.
- ↑ "Adverse behavioral response to clonazepam as a function of Verbal IQ-Performance IQ discrepancy". Epilepsy Research 1 (6): 347–356. 1987. doi:10.1016/0920-1211(87)90059-3. PMID 3504409.
- ↑ "Psychosis associated with clonazepam therapy for blepharospasm". The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 170 (2): 117–119. February 1982. doi:10.1097/00005053-198202000-00010. PMID 7057171.
- ↑ "Clonazepam-induced incontinence". Annals of Neurology 6 (1): 86. July 1979. doi:10.1002/ana.410060127. PMID 507767.
- ↑ "Urinary incontinence associated with clonazepam therapy". South African Medical Journal = Suid-Afrikaanse Tydskrif vir Geneeskunde 64 (7): 230. August 1983. PMID 6879368.
- ↑ "Overflow urinary incontinence due to carbamazepine". The Journal of Urology 134 (4): 758–759. October 1985. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(17)47428-3. PMID 4032590.
- ↑ "Disinhibitory reactions to benzodiazepines: a review". Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 49 (5): 519–523. May 1991. doi:10.1016/0278-2391(91)90180-T. PMID 2019899.
- ↑ "Clonazepam: new uses and potential problems". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 48 (Suppl): 50–56. October 1987. PMID 2889724.
- ↑ "Clonazepam in a focal-motor monkey model: efficacy, tolerance, toxicity, withdrawal, and management". Epilepsia 20 (6): 683–695. December 1979. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1979.tb04852.x. PMID 115680.
- ↑ "Use of barbiturates and benzodiazepines in treatment of epilepsy". Neurologic Clinics 4 (3): 617–632. August 1986. doi:10.1016/S0733-8619(18)30966-6. PMID 3528811.
- ↑ "Stressful reactions and panic attacks induced by flumazenil in chronic benzodiazepine users". Journal of Psychopharmacology 12 (2): 146–150. 1998. doi:10.1177/026988119801200205. PMID 9694026.
- ↑ Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology: Prescriber's Guide (5th ed.). San Diego, CA: Cambridge University Press. 2014. p. 139. ISBN 978-1-107-67502-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=Q7hkAwAAQBAJ&pg=PA139.
- ↑ "The benzodiazepine agonist clonazepam potentiates the effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid on alpha-MSH release from neurointermediate lobes in vitro". Life Sciences 40 (19): 1881–1887. May 1987. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(87)90046-4. PMID 3033417.
- ↑ "The effects of neuroleptics on the GABA-induced Cl- current in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons: differences between some neuroleptics". British Journal of Pharmacology 135 (6): 1547–1555. March 2002. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704608. PMID 11906969.
- ↑ "[Benzodiazepines in the treatment of epilepsy]". L'Encephale 9 (4 Suppl 2): 287B–292B. 1983. PMID 6373234.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsant effect of clonazepam in the dog: development of tolerance and physical dependence". Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie 278 (2): 249–260. December 1985. PMID 4096613.
- ↑ "Chronic clonazepam administration induces benzodiazepine receptor subsensitivity". Neuropharmacology 21 (1): 85–89. January 1982. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(82)90216-7. PMID 6278355.
- ↑ "Clonazepam in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy: a clinical short and long term follow-up study". Monographs in Neural Sciences. Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience 5: 153–159. 1980. doi:10.1159/000387498. ISBN 978-3-8055-0635-9. PMID 7033770.
- ↑ "Clonazepam withdrawal syndrome". Acta Neurologica 6 (2): 134–139. April 1984. PMID 6741654.
- ↑ "Interictal acute psychoses in temporal lobe epilepsy during withdrawal of anticonvulsant therapy". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 42 (8): 724–730. August 1979. doi:10.1136/jnnp.42.8.724. PMID 490178.
- ↑ "Clonazepam withdrawal psychosis". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 6 (3): 193. June 1986. doi:10.1097/00004714-198606000-00021. PMID 3711371.
- ↑ "Failure of carbamazepine to prevent clonazepam withdrawal status epilepticus". Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences 5 (3): 285–287. September 1984. doi:10.1007/BF02043959. PMID 6500901.
- ↑ "Clonazepam overdose resulting in cyclic coma". Clinical Toxicology 10 (4): 433–436. 1977. doi:10.3109/15563657709046280. PMID 862377.
- ↑ "Respiratory failure after clonazepam and amobarbital". The American Journal of Psychiatry 143 (11): 1495b–1495. November 1986. doi:10.1176/ajp.143.11.1495b. PMID 3777263.
- ↑ "Clonazepam, Prescription Marketed Drugs". http://drugsdb.eu/drug.php?d=Clonazepam&m=Contract%20Pharmacy%20Services-pa&id=52a03dbc-0510-40ec-8a33-15bf1c404622.xml.
- ↑ R. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2008, pp. 335-337.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 "Benzodiazepine dependence: focus on withdrawal syndrome". Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises 67 (6): 408–413. November 2009. doi:10.1016/j.pharma.2009.07.001. PMID 19900604.
- ↑ "Sleep and aging: 2. Management of sleep disorders in older people". CMAJ 176 (10): 1449–1454. May 2007. doi:10.1503/cmaj.070335. PMID 17485699.
- ↑ "Children of school age: the influence of antiepileptic drugs on behavior and intellect". Epilepsia 29 (Suppl 3): S15–S19. 1988. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1988.tb05805.x. PMID 3066616.
- ↑ "Dose-ranging studies of clonazepam in man". Psychopharmacology Communications 1 (1): 89–92. 1975. PMID 1223993.
- ↑ "Seizure management in acute hepatic porphyria: risks of valproate and clonazepam". Neurology 30 (6): 588–592. June 1980. doi:10.1212/WNL.30.6.588. PMID 6770287.
- ↑ "Safety of anticonvulsants in hepatic porphyrias". Neurology 31 (4): 480–484. April 1981. doi:10.1212/wnl.31.4.480. PMID 7194443.
- ↑ "Clonazepam treatment of chronic schizophrenia: negative results in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". The American Journal of Psychiatry 139 (12): 1627–1628. December 1982. doi:10.1176/ajp.139.12.1627. PMID 6756174.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine Equivalency Table: Benzodiazepine Equivalency". 28 April 2017. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2172250-overview#a1.
- ↑ 98.0 98.1 "Interactions between anticonvulsants". Proceedings of the Australian Association of Neurologists 12: 111–116. 1975. PMID 2912.
- ↑ "Clinically significant carbamazepine drug interactions: an overview". Epilepsia 28 (Suppl 3): S71–S76. 1987. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1157.1987.tb05781.x. PMID 3319544.
- ↑ "Phenytoin/clonazepam interaction". Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 7 (4): 481–484. August 1985. doi:10.1097/00007691-198512000-00022. PMID 4082246.
- ↑ 101.0 101.1 "Drug interactions during anticonvulsant therapy in childhood: diphenylhydantoin, primidone, phenobarbitone, clonazepam, nitrazepam, carbamazepin and dipropylacetate". Neuropadiatrie 8 (1): 29–41. February 1977. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1091502. PMID 321985.
- ↑ "[Laboratory controls in long-term treatment with anticonvulsive drugs (author's transl)]". Monatsschrift Fur Kinderheilkunde 125 (3): 122–128. March 1977. PMID 323695.
- ↑ "Influence of phenytoin and phenobarbital on the disposition of a single oral dose of clonazepam". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 28 (3): 368–375. September 1980. doi:10.1038/clpt.1980.175. PMID 7408397.
- ↑ "[Relationship between blood serum luminal and diphenylhydantoin level and the results of treatment and other clinical data in drug-resistant epilepsy]". Neurologia I Neurochirurgia Polska 14 (1): 39–45. 1980. PMID 7374896.
- ↑ "The effects of benzodiazepine use during pregnancy and lactation". Reproductive Toxicology 8 (6): 461–475. 1994. doi:10.1016/0890-6238(94)90029-9. PMID 7881198.
- ↑ "Effects of commonly used benzodiazepines on the fetus, the neonate, and the nursing infant". Psychiatric Services 53 (1): 39–49. January 2002. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.53.1.39. PMID 11773648. http://ps.psychiatryonline.org/cgi/content/full/53/1/39.
- ↑ "FDA clonazepam". https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/017533s053,020813s009lbl.pdf.
- ↑ "Enhancement of GABA binding by benzodiazepines and related anxiolytics". European Journal of Pharmacology 89 (3–4): 193–198. May 1983. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(83)90494-6. PMID 6135616.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine and beta-carboline modulation of GABA-stimulated 36Cl-influx in cultured spinal cord neurons". European Journal of Pharmacology 135 (2): 235–238. March 1987. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(87)90617-0. PMID 3034628.
- ↑ "[Pharmacological influences on the brain level and transport of GABA. I) Effect of various antipileptic drugs on brain levels of GABA]". Bollettino della Societa Italiana di Biologia Sperimentale 57 (8): 904–908. April 1981. PMID 7272065.
- ↑ "Effects of some anticonvulsant drugs on brain GABA level and GAD and GABA-T activities". Neurochemical Research 9 (2): 225–231. February 1984. doi:10.1007/BF00964170. PMID 6429560.
- ↑ "Drugs acting on amino acid neurotransmitters". Advances in Neurology 43: 687–706. 1986. PMID 2868623.
- ↑ "Mechanism of action of clonazepam in myoclonus in relation to effects on GABA and 5-HT". Advances in Neurology 43: 629–643. 1986. PMID 2418652.
- ↑ "Solubilization of peripheral benzodiazepine-binding sites from rat kidney". The Journal of Neuroscience 5 (11): 2889–2893. November 1985. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-11-02889.1985. PMID 2997409.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine Equivalency Table" based on NRHA Drug Newsletter, April 1985 and Benzodiazepines: How they Work & How to Withdraw (The Ashton Manual), 2002.[1]
- ↑ "What are the equivalent doses of oral benzodiazepines?" (in en-GB). https://www.sps.nhs.uk/articles/what-are-the-equivalent-doses-of-oral-benzodiazepines/.
- ↑ "Issues in the clinical use of benzodiazepines: potency, withdrawal, and rebound". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 65 (Suppl 5): 7–12. 2004. PMID 15078112.
- ↑ "Anticonvulsant drugs: mechanisms of action". Advances in Neurology 44: 713–736. 1986. PMID 2871724.
- ↑ "Benzodiazepine receptors on primary cultures of mouse astrocytes". Journal of Neurochemistry 36 (4): 1587–1589. April 1981. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00603.x. PMID 6267195.
- ↑ "[3HDiazepam binding in mammalian central nervous system: a pharmacological characterization"]. The Journal of Neuroscience 1 (2): 218–225. February 1981. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-02-00218.1981. PMID 6267221.
- ↑ "Effects of some benzodiazepines on the acetylcholine release in the anterior horn of the lateral cerebral ventricle of the cat". Acta Physiologica et Pharmacologica Bulgarica 8 (3): 59–66. 1982. PMID 6133407.
- ↑ "Suppression of prolactin secretion by benzodiazepines in vivo". Neuroendocrinology 34 (5): 369–373. 1982. doi:10.1159/000123330. PMID 6979001.
- ↑ "Inhibition of cold-induced TSH release by benzodiazepines". Brain Research 265 (2): 339–343. April 1983. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(83)90353-0. PMID 6405978.
- ↑ "Micromolar-affinity benzodiazepine receptors regulate voltage-sensitive calcium channels in nerve terminal preparations". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 81 (10): 3118–3122. May 1984. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.10.3118. PMID 6328498. Bibcode: 1984PNAS...81.3118T.
- ↑ (in en) The Treatment of Epilepsy. John Wiley & Sons. 2008. p. 366. ISBN 9780470752456. https://books.google.com/books?id=vFQFePTM-oAC&pg=PA366.
- ↑ 126.0 126.1 126.2 "Clonazepam". https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01068.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic consequences and clinical relevance of cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibition". Clinical Pharmacokinetics 38 (1): 41–57. January 2000. doi:10.2165/00003088-200038010-00003. PMID 10668858.
- ↑ "Monograph - Clonazepam -- Pharmacokinetics". Medscape. January 2006. http://www.medscape.com/druginfo/monograph?cid=med&drugid=14403&drugname=Clonazepam+Oral&monotype=monograph&secid=9.
- ↑ "An animal model for the study of drugs in the central nervous system". Proceedings of the Australian Association of Neurologists 13: 83–88. 1976. PMID 1029011.
- ↑ "A simple and sensitive gas chromatographic method for the determination of clonazepam in human plasma". Journal of Chromatography 116 (2): 445–450. January 1976. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)89915-X. PMID 1245581.
- ↑ "Pharmacokinetics of antiepileptic drugs". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. Supplementum 97: 17–27. 1983. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb01532.x. PMID 6143468.
- ↑ "Clonazepam pharmacokinetics, brain uptake, and receptor interactions". The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 48 (Suppl): 4–11. October 1987. PMID 2822672.
- ↑ "Improved micromethod for determination of underivatized clonazepam in serum by gas chromatography". Clinical Chemistry 24 (10): 1774–1777. October 1978. doi:10.1093/clinchem/24.10.1774. PMID 699288. http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/reprint/24/10/1774.pdf.
- ↑ Therapeutic Uses of Botulinum Toxin. Springer. 5 October 2007. ISBN 9781597452472. https://books.google.com/books?id=UIUhCmMtqq8C&pg=PA214.
- ↑ "Drug Abuse Warning Network, 2006: National Estimates of Drug-Related Emergency Department Visits". Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. 2006. http://www.samhsa.gov/data/DAWN/files/ED2006/DAWN2k6ED.htm.
- ↑ 136.0 136.1 "Clonazepam". Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. London: Pharmaceutical Press. http://www.medicinescomplete.com. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- ↑ "Burundanga y Clonazepan. El cóctel de pastillas que usaba una "viuda negra" para doblegar a sus incautos pretendientes" (in Spanish). La Nacion. 8 December 2022. https://www.lanacion.com.ar/seguridad/burundanga-y-clonazepan-el-arsenal-de-pastillas-que-usaba-la-viuda-negra-de-los-polvorines-para-nid07122022/.
- ↑ "Register of Medicinal Products". http://ravimiregister.ravimiamet.ee/en/default.aspx?pv=HumRavimid.Ravim&vid=55b06c4a-7c15-4164-8f23-74317a1c28ee.
- ↑ "Rivotril". 13 November 2020. https://www.nps.org.au/medicine-finder/rivotril-tablets.
Further reading
External links
 |