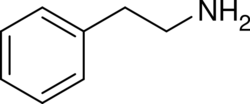
Chemistry:Substituted phenethylamine
| Substituted phenethylamine | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
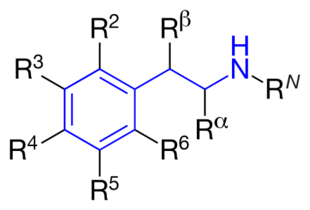 The structural formula of phenethylamine with marked substitution points. Phenethylamine is obtained when R2=R3=R4=R5=R6=RN=Rα=Rβ=H. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Chemical class | Substituted derivatives of phenethylamine |
Substituted phenethylamines (or simply phenethylamines) are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure;[note 1] the class is composed of all the derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents.
The structural formula of any substituted phenethylamine contains a phenyl ring that is joined to an amino (NH) group via a two-carbon sidechain. Hence, any substituted phenethylamine can be classified according to the substitution of hydrogen (H) atoms on phenethylamine's phenyl ring, sidechain, or amino group with a specific group of atoms.
Many substituted phenethylamines are psychoactive drugs which belong to a variety of different drug classes, including central nervous system stimulants (e.g., amphetamine), hallucinogens (e.g., 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine a.k.a. mescaline), 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine a.k.a. DOM), entactogen (e.g. MDA), appetite suppressants (e.g. phentermine), nasal decongestants and bronchodilators (e.g., levomethamphetamine and pseudoephedrine), antidepressants (e.g. bupropion and phenelzine), antiparkinson agents (e.g., selegiline), and vasopressors (e.g., ephedrine), among others.[1][2] Many of these psychoactive compounds exert their pharmacological effects primarily by modulating monoamine neurotransmitter systems; however, there is no mechanism of action or biological target that is common to all members of this subclass.
Numerous endogenous compounds – including hormones, catecholamines such as dopamine and noradrenaline, and many trace amines (e.g. adrenaline, phenethylamine itself, tyramine, thyronamine, and iodothyronamine) – are substituted phenethylamines. Several notable recreational drugs, such as MDMA (ecstasy), methamphetamine, and cathinone, are also members of the class. All of the substituted amphetamines and substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamines are substituted phenethylamines as well.
List of substituted phenethylamines
| Chemical
Structure |
Short Name | RN | Rα | Rβ | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | Full Name | Biologic activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| meta-Tyramine | OH | 3-hydroxyphenethylamine | Trace amine | |||||||
| para-Tyramine | OH | 4-hydroxyphenethylamine | Trace amine | |||||||
| Dopamine | OH | OH | 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine | Catecholamine neurotransmitter | ||||||
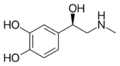
|
Epinephrine (Adrenaline) | CH3 | OH | OH | OH | β,3,4-trihydroxy-N-methylphenethylamine | Catecholamine neurotransmitter/Fight or Flight hormone | |||
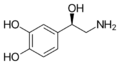
|
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) | OH | OH | OH | β,3,4-trihydroxyphenethylamine | Catecholamine neurotransmitter/Fight or Flight hormone | ||||

|
Norfenefrine | OH | OH | β,3-dihydroxyphenethylamine | Trace amine | |||||
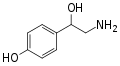
|
para-Octopamine | OH | OH | β,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine | Trace aminergic α-adrenoceptor agonist | |||||
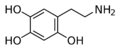
|
Oxidopamine | OH | OH | OH | 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenethylamine | neurotoxic agent for the dopamine and norepinephrine receptors | ||||
|
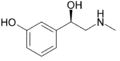
Phenylephrine | CH3 | OH | OH | β,3-dihydroxy-N-methylphenethylamine | α-adrenergic agonist; decongestant | ||||
|
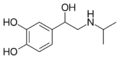
Isoprenaline | CH(CH3)2 | OH | OH | OH | β,3-dihydroxy-N-methylphenethylamine | β-adrenergic agonist; decongestant | |||
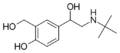
|
Salbutamol | C(CH3)3 | OH | CH2OH | OH | β,4-dihydroxy-3-hydroxymethyl-N-tert-butylphenethylamine | Short-action β2-adrenergic agonist | |||

|
β-Methylphenethylamine | CH3 | β-methylphenethylamine | Stimulant | ||||||

|
Amphetamine | CH3 | α-methylphenethylamine | Monoamine releasing agent; Stimulant | ||||||
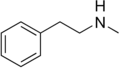
|
N-Methylphenethylamine | CH3 | N-methylphenethylamine | Trace amine; endogenous amphetamine isomer | ||||||
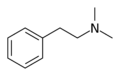
|
N,N-Dimethylphenethylamine | (CH3)2 | N,N-dimethylphenethylamine | Trivial effects (used as a food additive and flavoring agent) | ||||||
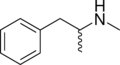
|
Methamphetamine | CH3 | CH3 | N-methylamphetamine; N,α-dimethylphenethylamine | Monoamine releasing agent; stimulant; neurotoxin | |||||
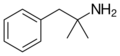
|
Phentermine | (CH3)2 | α-methylamphetamine; α,α-dimethylphenethylamine | Stimulant, anorectic | ||||||
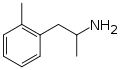
|
Ortetamine | CH3 | CH3 | 2-methylamphetamine; 2,α-dimethylphenethylamine | Stimulant, anorectic | |||||
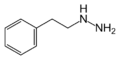
|
Phenelzine | NH2 | β-phenylethylhydrazine | Monoamine oxidase inhibitor | ||||||

|
Tranylcypromine | -CH2- | 2-phenylcyclopropylamine | Monoamine oxidase inhibitor | ||||||
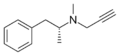
|
Selegiline | -CH2-C≡CH | CH3 | N,α-dimethyl-N-2-propynylphenethylamine | MAO-B selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor | |||||
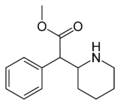
|
Methylphenidate | -CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2- | C(OCH3)=O | N,α-butylene-β-methoxycarbonylphenethylamine | NDRI; Stimulant | |||||

|
Ephedrine / Pseudoephedrine | CH3 | CH3 | OH | N-methyl-β-hydroxyamphetamine | Releasing agent; stimulant; decongestant | ||||

|
Cathine | CH3 | OH | d-β-hydroxyamphetamine | Moderately selective norepinephrine releasing agent | |||||
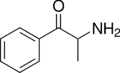
|
Cathinone | CH3 | =O | β-ketoamphetamine | Selective norepinephrine and dopamine releasing agent | |||||
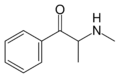
|
Methcathinone | CH3 | CH3 | =O | N-methylcathinone | Selective norepinephrine and dopamine releasing agent | ||||
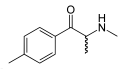
|
Mephedrone | CH3 | CH3 | =O | CH3 | 4-methylmethcathinone | Stimulant, unknown pharmacodynamic actions | |||
|
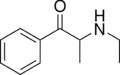
Ethcathinone | CH2CH3 | CH3 | =O | N-ethylcathinone | Stimulant and norepinephrine releasing agent | ||||
|
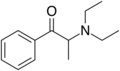
Amfepramone (diethylpropion) | C2H5, C2H5[note 2] | CH3 | =O | N-diethyl-β-ketoamphetamine | Anorectic | ||||
|
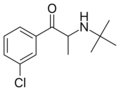
Bupropion | C(CH3)3 | CH3 | =O | Cl | 5-chloro-N-tert-butyl-β-ketoamphetamine | NDRI | |||
|
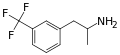
Norfenfluramine | CH3 | CF3 | 3-trifluoromethyl-amphetamine | SSRA | |||||

|
Fenfluramine | CH2CH3 | CH3 | CF3 | 3-trifluoromethyl-N-ethylamphetamine | SSRA | ||||
| 5-APB | CH3 | -CH=CH-O- | 5-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran | Stimulant, entactogen | ||||||
| 6-APB | CH3 | -O-CH=CH- | 6-(2-aminopropyl)benzofuran | Stimulant, entactogen | ||||||
| MDA | CH3 | -O-CH2-O- | 3,4-methylenedioxy-amphetamine | Stimulant, psychedelic, entactogen | ||||||
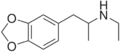
|
MDEA | CH2CH3 | CH3 | -O-CH2-O- | 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-ethylamphetamine | Psychedelic, entactogen, and releasing agent | ||||
|
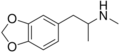
MDMA | CH3 | CH3 | -O-CH2-O- | 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine | Psychedelic, entactogen, and releasing agent | ||||
|
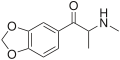
MDMC | CH3 | CH3 | =O | -O-CH2-O- | 3,4-methylenedioxymethcathinone | Psychedelic, entactogen, and releasing agent | |||
|
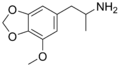
MMDA | CH3 | -O-CH2-O- | OCH3 | 5-methoxy-3,4-methylenedioxy-amphetamine | Stimulant, psychedelic and entactogen | ||||
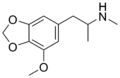
|
MMDMA | CH3 | CH3 | -O-CH2-O- | OCH3 | 5-methoxy-3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylamphetamine | Psychedelic, entactogen, and releasing agent | |||

|
Lophophine | -O-CH2-O- | OCH3 | 5-methoxy-3,4-methylenedioxyphenethylamine | Psychedelic and entactogen | |||||
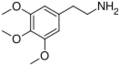
|
Mescaline | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenethylamine | Psychedelic and entactogen | ||||
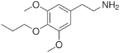
|
Proscaline | OCH3 | OCH2CH2CH3 | OCH3 | 2-(3,5-dimethoxy-4-propoxyphenyl)ethanamine | Psychedelic and entactogen | ||||
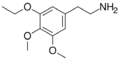
|
Metaescaline | OCH2CH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | 2-(3-ethoxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanamine | Psychedelic and entactogen | ||||
|
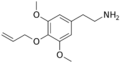
Allylescaline | OCH3 | OCH2CH1CH2 | OCH3 | 4-Allyloxy-3,5-dimethyloxyphenylethylamine | Psychedelic and entactogen | ||||
|
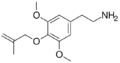
Methallylescaline | OCH3 | OCH2C(CH2CH3) | OCH3 | 4-Methallyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine | Psychedelic and entactogen | ||||
|
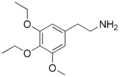
Asymbescaline | OCH2CH3 | OCH2CH3 | OCH3 | 3,4-Diethoxy-5-methoxyphenethylamine | Psychedelic and euphoriant | ||||
|
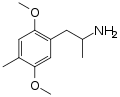
DOM | CH3 | OCH3 | CH3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine | Psychedelic | |||
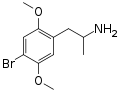
|
DOB | CH3 | OCH3 | Br | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine | Psychedelic | |||
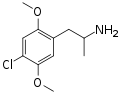
|
DOC | CH3 | OCH3 | Cl | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloroamphetamine | Psychedelic | |||
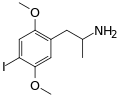
|
DOI | CH3 | OCH3 | I | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine | Psychedelic | |||
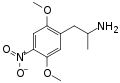
|
DON | CH3 | OCH3 | NO2 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitroamphetamine | Stimulant | |||
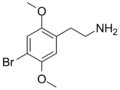
|
2C-B | OCH3 | Br | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenethylamine | Psychedelic, stimulant, entactogen and euphoriant | ||||

|
βk-2C-B | =O | OCH3 | Br | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo-β-ketophenethylamine | Psychedelic, stimulant, entactogen and euphoriant | |||

|
2C-C | OCH3 | Cl | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-chlorophenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||
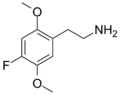
|
2C-F | OCH3 | F | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-fluorophenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||

|
2C-I | OCH3 | I | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenethylamine | Psychedelic, stimulant | ||||
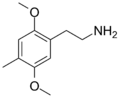
|
2C-D | OCH3 | CH3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylphenethylamine | Psychedelic, stimulant | ||||
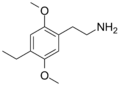
|
2C-E | OCH3 | CH2-CH3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylphenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||
|
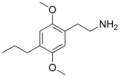
2C-P | OCH3 | CH2-CH3-CH3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylphenethylamine | Entactogen, euphoriant and Psychedelic | ||||
|
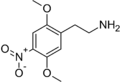
2C-N | OCH3 | NO2 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitrophenethylamine | euphoriant | ||||
|
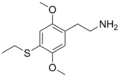
2C-T-2 | OCH3 | S-CH2CH3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-ethylthio-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||
|
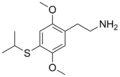
2C-T-4 | OCH3 | S-CH(CH3)2 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-isopropylthio-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||
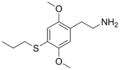
|
2C-T-7 | OCH3 | S-CH2CH2CH3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-propylthio-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||
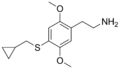
|
2C-T-8 | OCH3 | S-CH2-C3H5 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-cyclopropylmethylthio-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||

|
2C-T-19 | OCH3 | S-C(CH3)3 | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-tert-butylthio-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | ||||
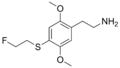
|
2C-T-21 | OCH3 | S-CH2-CH2-F | OCH3 | 2,5-dimethoxy-4-(2-fluoroethylthio)-phenethylamine | Psychedelic and euphoriant | ||||
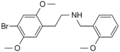
|
25B-NBOMe[3] | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | Br | OCH3 | 2-(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||

|
25C-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | Cl | OCH3 | 2-(4-chloro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
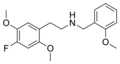
|
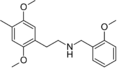
25F-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | F | OCH3 | 2-(4-fluoro-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
|
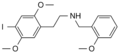
25I-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | I | OCH3 | 2-(4-iodo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
|
25D-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | CH2 | OCH3 | 2-(4-methyl-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
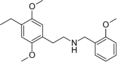
|
25E-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | CH2-CH3 | OCH3 | 2-(4-ethyl-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
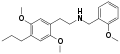
|
25P-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | CH2-CH3-CH3 | OCH3 | 2-(4-propyl-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-N-[(2-methoxyphenyl)methyl]ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
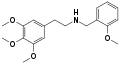
|
Mescaline-NBOMe | CH2-C6H4-OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | OCH3 | N-(2-Methoxybenzyl)-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)ethanamine | Psychedelic | |||
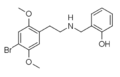
|
25B-NBOH | CH2–C6H4–OH | OCH3 | Br | OCH3 | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromo-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | |||
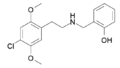
|
25C-NBOH | CH2–C6H4–OH | OCH3 | Cl | OCH3 | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-chloro-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | |||
|
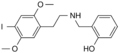
25I-NBOH | CH2–C6H4–OH | OCH3 | I | OCH3 | N-(2-hydroxybenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | |||
|
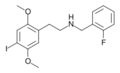
25I-NBF | CH2–C6H4–F | OCH3 | I | OCH3 | N-(2-fluorobenzyl)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo-phenethylamine | Psychedelic | |||
| Short Name | RN | Rα | Rβ | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | Full Name | Biologic activity | |
Detection
| method | Requirement |
|---|---|
| UV spectrometry | Reagent needed |
See also
- Substituted amphetamine
- Substituted methylenedioxyphenethylamine
- Substituted cathinone
- Substituted phenylmorpholine
- 2Cs, DOx, 25-NB
- Substituted tryptamine
- PiHKAL
Notes
- ↑ In other words, all of the compounds that belong to this class are structural analogs of phenethylamine.
- ↑ Two ethyl groups attached to the amine group
References
- ↑ Inan, Funda; Brunt, Tibor M.; Contrucci, Ramon R.; Hondebrink, Laura; Franssen, Eric J. F. (2020). "Novel Phenethylamines and Their Potential Interactions With Prescription Drugs: A Systematic Critical Review". Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 42 (2): 271–281. doi:10.1097/ftd.0000000000000725. ISSN 0163-4356. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/ftd.0000000000000725.
- ↑ Wills, Brandon; Erickson, Timothy (2012-02-02). "Psychoactive Phenethylamine, Piperazine, and Pyrrolidinophenone Derivatives". Medical Toxicology of Drug Abuse: 156–192. doi:10.1002/9781118105955.ch10. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/9781118105955.ch10.
- ↑ Custodio, Raly James Perez; Sayson, Leandro Val; Botanas, Chrislean Jun; Abiero, Arvie; You, Kyung Yi; Kim, Mikyung; Lee, Hyun Jun; Yoo, Sung Yeun et al. (2019). "25B-NBOMe, a novel N-2-methoxybenzyl-phenethylamine (NBOMe) derivative, may induce rewarding and reinforcing effects via a dopaminergic mechanism: Evidence of abuse potential" (in en). Addiction Biology 25 (6): e12850. doi:10.1111/adb.12850. ISSN 1369-1600. PMID 31749223.
 |