Chemistry:CI-1017
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
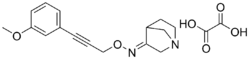
| Formula | C18H20N2O6 |
| Molar mass | 360.366 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
CI-1017 is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist which is selective for and is approximately equipotent at the M1 and M4 receptors, with 20-30-fold lower affinity for the M2, M3, and M5 subtypes[1] It is the (R)-enantiomer of the racemic compound PD-142,505.[1]
In animals CI-1017 improves learning and memory and increases the electrical activity of the hippocampus through activation of the M1 receptor, while minimally producing parasympathetic side effects and only at very high doses.[2][3][4] It also inhibits production of amyloidogenic A beta peptide and increases secretion of soluble amyloid precursor protein via stimulation of the M1 receptor as well.[3] Based on these data, it was hypothesized that CI-1017 could not only treat the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease, but could also potentially slow its progression.[3] It was tested in clinical trials for this purpose in the early 2000s but was abandoned due to lack of efficacy.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Design and synthesis of m1-selective muscarinic agonists: (R)-(−)-(Z)-1-Azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-one, O-(3-(3'-methoxyphenyl)-2-propynyl)oxime maleate (CI-1017), a functionally m1-selective muscarinic agonist". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 41 (14): 2524–36. July 1998. doi:10.1021/jm960683m. PMID 9651157.
- ↑ "The M1 muscarinic agonist CI-1017 facilitates trace eyeblink conditioning in aging rabbits and increases the excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurons". Journal of Neuroscience 20 (2): 783–90. January 2000. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-02-00783.2000. PMID 10632607.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "CI-1017, a functionally M1-selective muscarinic agonist: design, synthesis, and preclinical pharmacology". Pharmaceutica Acta Helvetiae 74 (2–3): 141–8. March 2000. doi:10.1016/s0031-6865(99)00027-8. PMID 10812951.
- ↑ "Modulation of cholinergic transmission enhances excitability of hippocampal pyramidal neurons and ameliorates learning impairments in aging animals". Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 80 (3): 223–33. November 2003. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2003.08.004. PMID 14521865.
- ↑ "Model-based drug development". Clin Pharmacol Ther 82 (1): 21–32. 2007. doi:10.1038/sj.clpt.6100235. PMID 17522597.
 |

