Astronomy:Kepler-440b
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovery site | Kepler Space Observatory |
| Discovery date | 2015[2] |
| Transit | |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| 0.24200 AU (36,203,000 km) | |
| Eccentricity | >0.340 |
| Orbital period | 101.11141000 d |
| Inclination | 89.930 |
| Star | Kepler-440 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 1.860 R⊕ |
| Physics | 273 K (0 °C; 32 °F).[3] |
Kepler-440b (also known by its Kepler Object of Interest designation KOI-4087.01) is a confirmed super-Earth exoplanet orbiting within the habitable zone of Kepler-440, about 850 light-years (261 pc) from Earth.[1] The planet was discovered by NASA's Kepler spacecraft using the transit method, in which the dimming effect that a planet causes as it crosses in front of its star is measured. NASA announced the confirmation of the exoplanet on 6 January 2015.[4]
Confirmed exoplanet
Kepler-440b is a [super-Earth] with a radius 1.86 times that of Earth. The planet orbits Kepler-440 once every 101.1 days.[1]
Habitability
The planet was announced as being located within the habitable zone of Kepler-440, a region where liquid water could exist on the surface of the planet.[1]
| Notable Exoplanets – Kepler Space Telescope |
|---|
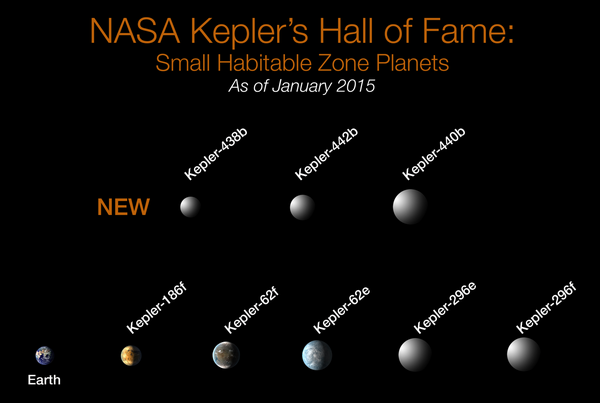
Confirmed small exoplanets in habitable zones.
(Kepler-62e, Kepler-62f, Kepler-186f, Kepler-296e, Kepler-296f, Kepler-438b, Kepler-440b, Kepler-442b) (Kepler Space Telescope; 6 January 2015).[4] |
| Earth | Kepler-440b |
|---|---|

|

|
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Torres, Guillermo; Kipping, David M.; Fressin, Francois; Caldwell, Douglas A.; Twicken, Joseph D.; Ballard, Sarah; Batalha, Natalie M.; Bryson, Stephen T. et al. (2015). "Validation of Twelve Small Kepler Transiting Planets in the Habitable Zone". The Astrophysical Journal 800 (2): 99. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/800/2/99. Bibcode: 2015ApJ...800...99T.
- ↑ Staff (2015). "Planet Kepler-440 b". Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. https://exoplanet.eu/catalog/kepler_440_b--2343/. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ↑ "HEC: Data of Potential Habitable Worlds". http://phl.upr.edu/projects/habitable-exoplanets-catalog/data.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Clavin, Whitney; Chou, Felicia; Johnson, Michele (6 January 2015). "NASA's Kepler Marks 1,000th Exoplanet Discovery, Uncovers More Small Worlds in Habitable Zones". NASA. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2015-003.
External links
- NASA – Mission overview.
- NASA – Kepler Discoveries – Summary Table.
- NASA – Kepler-440b at The NASA Exoplanet Archive.
- NASA – Kepler-440b at The Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia.
- Habitable Exolanets Catalog at UPR-Arecibo.
Coordinates: ![]() 19h 01m 23.99s, +41° 27′ 07.94″
19h 01m 23.99s, +41° 27′ 07.94″
 |





