Chemistry:Beryllium iodide
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Beryllium iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| BeI2 | |
| Molar mass | 262.821 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless needle-like crystals |
| Density | 4.325 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 480 °C (896 °F; 753 K) |
| Boiling point | 590 °C (1,094 °F; 863 K)[1] |
| reacts with water[1][citation needed] | |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in CS2 Soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether[2] |
| Structure | |
| orthorhombic | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
71.14 J/(mol × K) |
Std molar
entropy (S |
130 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-192.62 kJ/mol |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚)
|
-210 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
19 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | see Berylliosis |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.002 mg/m3 C 0.005 mg/m3 (30 minutes), with a maximum peak of 0.025 mg/m3 (as Be)[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca C 0.0005 mg/m3 (as Be)[3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [4 mg/m3 (as Be)][3] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Beryllium fluoride Beryllium chloride Beryllium bromide |
Other cations
|
magnesium iodide calcium iodide strontium iodide barium iodide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Beryllium iodide is the inorganic compound with the formula BeI2. It is a hygroscopic white solid.
Reactions
Beryllium iodide can be prepared by reacting beryllium metal with elemental iodine at temperatures of 500 °C to 700 °C:[1]
Beryllium iodide is also formed when beryllium carbide reacts with hydrogen iodide in the gas phase:
Beryllium iodide reacts with fluorine giving beryllium fluoride and fluorides of iodine, with chlorine giving beryllium chloride, and with bromine giving beryllium bromide.
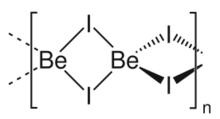
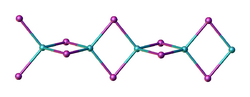
Structure
Two forms (polymorphs) of BeI2 are known. Both structures consist tetrahedral Be2+ centers interconnected by doubly bridging iodide ligands. One form consist of edge-sharing polytetrahedra. The other form resembles zinc iodide with interconnected adamantane-like cages.[4]
Applications
Beryllium iodide can be used in the preparation of high-purity beryllium by the decomposition of the compound on a hot tungsten filament.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Perry, Dale L.; Phillips, Sidney L. (1995), Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, CRC Press, pp. 63, ISBN 0-8493-8671-3, https://books.google.com/books?id=0fT4wfhF1AsC&q=%22beryllium+iodide%22+properties, retrieved 2007-12-10
- ↑ Parsons, Charles Lathrop (1909), The Chemistry and Literature of Beryllium, Easton, Pa.: Chemical Publishing, pp. 22–23, https://books.google.com/books?id=7MxAAAAAIAAJ&q=%22beryllium+iodide%22&pg=PA21, retrieved 2007-12-10
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0054". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0054.html.
- ↑ Troyanov, S.I. (2000). "Crystal Modifications of Beryllium Dihalides BeCl2, BeBr2 and BeI2". Zhurnal Neorganicheskoi Khimii 45: 1619–1624.
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |


