Astronomy:UX Antliae
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Corona Borealis |
| Right ascension | 10h 57m 9.051s[2] |
| Declination | −37° 23′ 55.06″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.85 - 18.0[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | C(F)[4] |
| Variable type | R CrB[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 27.83[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -3.8[2] mas/yr Dec.: 2.3[2] mas/yr |
| Distance | ~25,000[4] pc |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | ~−5[4] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.722[7] M☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.5[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 7,000[7] K |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
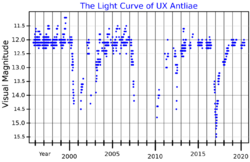
UX Antliae is a post-AGB and R Coronae Borealis variable star that has a base apparent magnitude of around 11.85, with irregular dimmings down to below magnitude 18.0.[8]
Researchers David Kilkenny and J.E. Westerhuys of the South African Astronomical Observatory confirmed that UX Antliae was an R Coronae Borealis variable in 1990 after noting the similarity of its spectrum to the RCB star W Mensae.[9] It had been suspected of being one since 1940, but had been little-studied and exhibited no characteristic declines between 1975 and 1990.[4]
Assuming that its absolute magnitude is around -5, it has been estimated as lying 25000 parsecs distant from Earth.[4] Kilkenny and Westerhuys noted that its spectrum fit with that of a star of spectral class F, although was deficient in hydrogen.[9] It has around 70% the mass of the Sun and an effective (surface) temperature of around 7000 K.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ "Download Data". AAVSO. https://www.aavso.org/data-download.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P. et al. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 355: L27. doi:10.1888/0333750888/2862. Bibcode: 2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ↑ Otero, Sebastian (23 November 2012). "UX Antliae". The International Variable Star Index. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=31899.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Lawson, W. A.; Cottrell, P. L.; Kilkenny, D.; Gilmore, A. C.; Kilmartin, P. M.; Marang; Roberts; Van Wyk (1994). "The Variability of the R-Coronae Star Ux-Antliae at Maximum Light". Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 271 (4): 919–23. doi:10.1093/mnras/271.4.919. Bibcode: 1994MNRAS.271..919L.
- ↑ Hema, B. P.; Pandey, Gajendra; Lambert, David L. (2012). "The Galactic R Coronae Borealis Stars: The C2 Swan Bands, the Carbon Problem, and the 12C/13C Ratio". The Astrophysical Journal 747 (2): 102. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/747/2/102. Bibcode: 2012ApJ...747..102H.
- ↑ White, Russel J.; Gabor, Jared M.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2007). "High-Dispersion Optical Spectra of Nearby Stars Younger Than the Sun". The Astronomical Journal 133 (6): 2524. doi:10.1086/514336. Bibcode: 2007AJ....133.2524W.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Stasińska, G.; Szczerba, R.; Schmidt, M.; Siódmiak, N. (2006). "Post-AGB stars as testbeds of nucleosynthesis in AGB stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics 450 (2): 701. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053553. Bibcode: 2006A&A...450..701S.
- ↑ Otero, Sebastian (23 November 2012). "V4199 Sgr". The International Variable Star Index. http://www.aavso.org/vsx/index.php?view=detail.top&oid=31899.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Kilkenny, D.; Westerhuys, J. E. (1990). "Spectroscopy of 'RCB' stars-IV. UX ANT". The Observatory 110: 90–92. Bibcode: 1990Obs...110...90K.
External links
"Post-AGB Object 279.064 +20.120". www.ncac.torun.pl. http://www.ncac.torun.pl/postagb?lang=en&branch=postagbworld&id=2&l=279.064&b=20.12.
"Light Curve of UX Ant". www.kusastro.kyoto-u.ac.jp. http://www.kusastro.kyoto-u.ac.jp/vsnet/LCs/index/ANTUX.html.
 |