Biology:Hfq binding sRNA
| isrA Hfq binding RNA | |
|---|---|
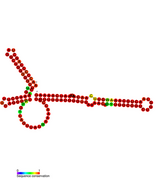
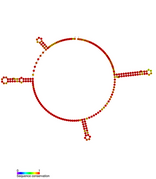
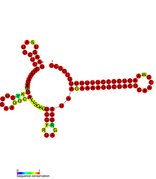
 Predicted secondary structure of isrA Hfq binding RNA | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | isrA |
| Rfam | RF01385 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | gene, sRNA |
| Domain(s) | Enterobacteriaceae |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
An Hfq binding sRNA is an sRNA that binds the bacterial RNA binding protein called Hfq. A number of bacterial small RNAs which have been shown to bind to Hfq have been characterised (see list). Many of these RNAs share a similar structure composed of three stem-loops.[1] Several studies have expanded this list, and experimentally validated a total of 64 Hfq binding sRNA in Salmonella Typhimurium.[2][3][4] A transcriptome wide study on Hfq binding sites in Salmonella mapped 126 Hfq binding sites within sRNAs.[5] Genomic SELEX has been used to show that Hfq binding RNAs are enriched in the sequence motif 5′-AAYAAYAA-3′.[6] Genome-wide study identified 40 candidate Hfq-dependent sRNAs in plant pathogen Erwinia amylovora. 12 of them were confirmed by Northern blot.[7]
Bacterial Hfq binding sRNAs
- DicF RNA
- DsrA RNA
- FnrS RNA
- GadY RNA
- GcvB RNA
- IsrJ RNA[4]
- MicA RNA / SraD RNA
- MicC RNA
- MicF RNA
- OmrA RNA / OmrB RNA / RygA RNA / RygB RNA / SraE RNA
- OxyS RNA
- Qrr RNA
- RmA RNA
- RprA RNA
- RybB RNA
- RydC RNA
- RyeB RNA
- CyaR RNA
- RyeF
- RyhB RNA
- SgrS RNA
- Spot 42 RNA
- SraH RNA
- SraJ RNA
- SroB RNA / MicM RNA / RybC
- SroC RNA
References
- ↑ "Global analysis of small RNA and mRNA targets of Hfq". Mol. Microbiol. 50 (4): 1111–1124. 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03734.x. PMID 14622403.
- ↑ "A small non-coding RNA of the invasion gene island (SPI-1) represses outer membrane protein synthesis from the Salmonella core genome". Molecular Microbiology 66 (5): 1174–1191. December 2007. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05991.x. PMID 17971080.
- ↑ Burkholder, William F., ed (2008). "Deep Sequencing Analysis of Small Noncoding RNA and mRNA Targets of the Global Post-Transcriptional Regulator, Hfq". PLOS Genetics 4 (8): e1000163. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000163. PMID 18725932.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Small RNAs encoded within genetic islands of Salmonella typhimurium show host-induced expression and role in virulence". Nucleic Acids Research 36 (6): 1913–1927. April 2008. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn050. PMID 18267966.
- ↑ "Global RNA recognition patterns of post-transcriptional regulators Hfq and CsrA revealed by UV crosslinking in vivo.". EMBO J 35 (9): 991–1011. 2016. doi:10.15252/embj.201593360. PMID 27044921.
- ↑ "Genomic SELEX for Hfq-binding RNAs identifies genomic aptamers predominantly in antisense transcripts". Nucleic Acids Res 38 (11): 3794–3808. 2010. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq032. PMID 20348540.
- ↑ Zeng, Quan; Sundin, George W. (2014-01-01). "Genome-wide identification of Hfq-regulated small RNAs in the fire blight pathogen Erwinia amylovora discovered small RNAs with virulence regulatory function". BMC Genomics 15 (1): 414. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-414. ISSN 1471-2164. PMID 24885615.
Further reading
- De Lay, N.; Schu, D. J.; Gottesman, S. (2013). "Bacterial Small RNA-based Negative Regulation: Hfq and Its Accomplices". Journal of Biological Chemistry 288 (12): 7996–8003. doi:10.1074/jbc.R112.441386. PMID 23362267.
- Peng, Y.; Soper, T. J.; Woodson, S. A. (2013). "Positional effects of AAN motifs in rpoS regulation by sRNAs and Hfq". Journal of Molecular Biology 426 (2): 275–285. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2013.08.026. PMID 24051417.
External links
 |