Sporadic group
| Algebraic structure → Group theory Group theory |
|---|
 |
In mathematics, a sporadic group is one of the 26 exceptional groups found in the classification of finite simple groups.
A simple group is a group G that does not have any normal subgroups except for the trivial group and G itself. The classification theorem states that the list of finite simple groups consists of 18 countably infinite families[lower-alpha 1] plus 26 exceptions that do not follow such a systematic pattern. These 26 exceptions are the sporadic groups. They are also known as the sporadic simple groups, or the sporadic finite groups. Because it is not strictly a group of Lie type, the Tits group is sometimes regarded as a sporadic group,[1] in which case there would be 27 sporadic groups.
The monster group, or friendly giant, is the largest of the sporadic groups, and all but six of the other sporadic groups are subquotients of it.[2]
Names
Five of the sporadic groups were discovered by Émile Mathieu in the 1860s and the other twenty-one were found between 1965 and 1975. Several of these groups were predicted to exist before they were constructed. Most of the groups are named after the mathematician(s) who first predicted their existence. The full list is:[1][3][4]
- Mathieu groups M11 (M11), M12 (M12), M22 (M22), M23 (M23), M24 (M24)
- Janko groups J1 (J1), J2 or HJ (J2), J3 or HJM (J3), J4 (J4)
- Conway groups Co1 (Co1), Co2 (Co2), Co3 (Co3)
- Fischer groups Fi22 (Fi22), Fi23 (Fi23), Fi24′ or F3+ (Fi24)
- Higman-Sims group HS
- McLaughlin group McL
- Held group He or F7+ or F7
- Rudvalis group Ru
- Suzuki group Suz or F3−
- O'Nan group O'N (ON)
- Harada-Norton group HN or F5+ or F5
- Lyons group Ly
- Thompson group Th or F3|3 or F3
- Baby Monster group B or F2+ or F2
- Fischer-Griess Monster group M or F1
Various constructions for these groups were first compiled in (Conway Curtis), including character tables, individual conjugacy classes and lists of maximal subgroup, as well as Schur multipliers and orders of their outer automorphisms. These are also listed online at (Wilson Parker), updated with their group presentations and semi-presentations. The degrees of minimal faithful representation or Brauer characters over fields of characteristic p ≥ 0 for all sporadic groups have also been calculated, and for some of their covering groups. These are detailed in (Jansen 2005).
A further exception in the classification of finite simple groups is the Tits group T, which is sometimes considered of Lie type[5] or sporadic — it is almost but not strictly a group of Lie type[6] — which is why in some sources the number of sporadic groups is given as 27, instead of 26.[7][8] In some other sources, the Tits group is regarded as neither sporadic nor of Lie type, or both.[9][citation needed] The Tits group is the (n = 0)-member 2F4(2)′ of the infinite family of commutator groups 2F4(22n+1)′; thus in a strict sense not sporadic, nor of Lie type. For n > 0 these finite simple groups coincide with the groups of Lie type 2F4(22n+1), also known as Ree groups of type 2F4.
The earliest use of the term sporadic group may be (Burnside 1911) where he comments about the Mathieu groups: "These apparently sporadic simple groups would probably repay a closer examination than they have yet received."
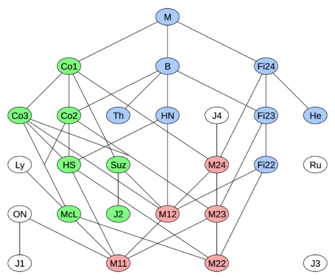
The diagram at right is based on (Ronan 2006). It does not show the numerous non-sporadic simple subquotients of the sporadic groups.
Organization
Happy Family
Of the 26 sporadic groups, 20 can be seen inside the monster group as subgroups or quotients of subgroups (sections). These twenty have been called the happy family by Robert Griess, and can be organized into three generations.[10][lower-alpha 2]
First generation (5 groups): the Mathieu groups
Mn for n = 11, 12, 22, 23 and 24 are multiply transitive permutation groups on n points. They are all subgroups of M24, which is a permutation group on 24 points.[11]
Second generation (7 groups): the Leech lattice
All the subquotients of the automorphism group of a lattice in 24 dimensions called the Leech lattice:[12]
- Co1 is the quotient of the automorphism group by its center {±1}
- Co2 is the stabilizer of a type 2 (i.e., length 2) vector
- Co3 is the stabilizer of a type 3 (i.e., length √6) vector
- Suz is the group of automorphisms preserving a complex structure (modulo its center)
- McL is the stabilizer of a type 2-2-3 triangle
- HS is the stabilizer of a type 2-3-3 triangle
- J2 is the group of automorphisms preserving a quaternionic structure (modulo its center).
Third generation (8 groups): other subgroups of the Monster
Consists of subgroups which are closely related to the Monster group M:[13]
- B or F2 has a double cover which is the centralizer of an element of order 2 in M
- Fi24′ has a triple cover which is the centralizer of an element of order 3 in M (in conjugacy class "3A")
- Fi23 is a subgroup of Fi24′
- Fi22 has a double cover which is a subgroup of Fi23
- The product of Th = F3 and a group of order 3 is the centralizer of an element of order 3 in M (in conjugacy class "3C")
- The product of HN = F5 and a group of order 5 is the centralizer of an element of order 5 in M
- The product of He = F7 and a group of order 7 is the centralizer of an element of order 7 in M.
- Finally, the Monster group itself is considered to be in this generation.
(This series continues further: the product of M12 and a group of order 11 is the centralizer of an element of order 11 in M.)
The Tits group, if regarded as a sporadic group, would belong in this generation: there is a subgroup S4 ×2F4(2)′ normalising a 2C2 subgroup of B, giving rise to a subgroup 2·S4 ×2F4(2)′ normalising a certain Q8 subgroup of the Monster. 2F4(2)′ is also a subquotient of the Fischer group Fi22, and thus also of Fi23 and Fi24′, and of the Baby Monster B. 2F4(2)′ is also a subquotient of the (pariah) Rudvalis group Ru, and has no involvements in sporadic simple groups except the ones already mentioned.
Pariahs
The six exceptions are J1, J3, J4, O'N, Ru and Ly, sometimes known as the pariahs.[14][15]
Table of the sporadic group orders (with Tits group)
| Group | Discoverer | [16] Year |
Generation
|
[4][17] Order |
[1][4] Factorized order |
[18] Minimal faithful Brauer character |
[19][20] [math]\displaystyle{ (a, b, ab) }[/math] Generators
|
[20][lower-alpha 3] [math]\displaystyle{ \langle\langle a,b \mid o(z)\rangle\rangle }[/math] Semi-presentation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M or F1 | Fischer, Griess | 1973 | 3 3rd | align=right | 808017424794512875 |
≈ 8×1053 | 246 × 320 × 59 × 76 × 112 × 133 × 17 × 19 × 23 × 29 × 31 × 41 × 47 × 59 × 71 | 196883 | 2A, 3B, 29 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^{4}(ab^{2})^{2}\bigr) = 50 }[/math] |
| B or F2 | Fischer | 1973 | 3 3rd | align=right | 4154781481226426 |
≈ 4×1033 | 241 × 313 × 56 × 72 × 11 × 13 × 17 × 19 × 23 × 31 × 47 | 4371 | 2C, 3A, 55 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^2 (abab^2)^2 ab^2\bigr) = 23 }[/math] |
| Fi24 or F3+ | Fischer | 1971 | 3 3rd | align=right | 1255205 |
≈ 1×1024 | 221 × 316 × 52 × 73 × 11 × 13 × 17 × 23 × 29 | 8671 | 2A, 3E, 29 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^3 b\bigr) = 33 }[/math] |
| Fi23 | Fischer | 1971 | 3 3rd | align=right | 4089470473293004800 | ≈ 4×1018 | 218 × 313 × 52 × 7 × 11 × 13 × 17 × 23 | 782 | 2B, 3D, 28 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(a^{bb}(ab)^{14}\bigr) = 5 }[/math] |
| Fi22 | Fischer | 1971 | 3 3rd | align=right | 64561751654400 | ≈ 6×1013 | 217 × 39 × 52 × 7 × 11 × 13 | 78 | 2A, 13, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^2 (abab^2)^2 ab^2\bigr) = 12 }[/math] |
| Th or F3 | Thompson | 1976 | 3 3rd | align=right | 90745943887872000 | ≈ 9×1016 | 215 × 310 × 53 × 72 × 13 × 19 × 31 | 248 | 2, 3A, 19 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^{3}b\bigr) = 21 }[/math] |
| Ly | Lyons | 1972 | 4 Pariah | align=right | 51765179004000000 | ≈ 5×1016 | 28 × 37 × 56 × 7 × 11 × 31 × 37 × 67 | 2480 | 2, 5A, 14 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(ababab^2\bigr) = 67 }[/math] |
| HN or F5 | Harada, Norton | 1976 | 3 3rd | align=right | 273030912000000 | ≈ 3×1014 | 214 × 36 × 56 × 7 × 11 × 19 | 133 | 2A, 3B, 22 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a, b]\bigr) = 5 }[/math] |
| Co1 | Conway | 1969 | 2 2nd | align=right | 4157776806543360000 | ≈ 4×1018 | 221 × 39 × 54 × 72 × 11 × 13 × 23 | 276 | 2B, 3C, 40 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(ab(abab^{2})^{2}\bigr) = 42 }[/math] |
| Co2 | Conway | 1969 | 2 2nd | align=right | 42305421312000 | ≈ 4×1013 | 218 × 36 × 53 × 7 × 11 × 23 | 23 | 2A, 5A, 28 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a,b]\bigr) = 4 }[/math] |
| Co3 | Conway | 1969 | 2 2nd | align=right | 495766656000 | ≈ 5×1011 | 210 × 37 × 53 × 7 × 11 × 23 | 23 | 2A, 7C, 17 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((uvv)^{3}(uv)^{6}\bigr) = 5 }[/math][lower-alpha 4] |
| ON or O'N | O'Nan | 1976 | 4 Pariah | align=right | 460815505920 | ≈ 5×1011 | 29 × 34 × 5 × 73 × 11 × 19 × 31 | 10944 | 2A, 4A, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(abab(b^{2}(b^{2})^{abab})^{5}\bigr) = 5 }[/math] |
| Suz | Suzuki | 1969 | 2 2nd | align=right | 448345497600 | ≈ 4×1011 | 213 × 37 × 52 × 7 × 11 × 13 | 143 | 2B, 3B, 13 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a, b]\bigr) = 15 }[/math] |
| Ru | Rudvalis | 1972 | 4 Pariah | align=right | 145926144000 | ≈ 1×1011 | 214 × 33 × 53 × 7 × 13 × 29 | 378 | 2B, 4A, 13 | [math]\displaystyle{ o(abab^{2}) = 29 }[/math] |
| He or F7 | Held | 1969 | 3 3rd | align=right | 4030387200 | ≈ 4×109 | 210 × 33 × 52 × 73 × 17 | 51 | 2A, 7C, 17 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(ab^{2}abab^{2}ab^{2}\bigr) = 10 }[/math] |
| McL | McLaughlin | 1969 | 2 2nd | align=right | 898128000 | ≈ 9×108 | 27 × 36 × 53 × 7 × 11 | 22 | 2A, 5A, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^2 (abab^2)^2 ab^2\bigr) = 7 }[/math] |
| HS | Higman, Sims | 1967 | 2 2nd | align=right | 44352000 | ≈ 4×107 | 29 × 32 × 53 × 7 × 11 | 22 | 2A, 5A, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o(abab^{2}) = 15 }[/math] |
| J4 | Janko | 1976 | 4 Pariah | align=right | 86775571046077562880 | ≈ 9×1019 | 221 × 33 × 5 × 7 × 113 × 23 × 29 × 31 × 37 × 43 | 1333 | 2A, 4A, 37 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(abab^2\bigr) = 10 }[/math] |
| J3 or HJM | Janko | 1968 | 4 Pariah | align=right | 50232960 | ≈ 5×107 | 27 × 35 × 5 × 17 × 19 | 85 | 2A, 3A, 19 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a, b]\bigr) = 9 }[/math] |
| J2 or HJ | Janko | 1968 | 2 2nd | align=right | 604800 | ≈ 6×105 | 27 × 33 × 52 × 7 | 14 | 2B, 3B, 7 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a, b]\bigr) = 12 }[/math] |
| J1 | Janko | 1965 | 4 Pariah | align=right | 175560 | ≈ 2×105 | 23 × 3 × 5 × 7 × 11 × 19 | 56 | 2, 3, 7 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(abab^2\bigr) = 19 }[/math] |
| T or 2F4(2)′ | Tits | 1964 | 3 3rd | align=right | 17971200 | ≈ 2×107 | 211 × 33 × 52 × 13 | 104[21] | 2A, 3, 13 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a, b]\bigr) = 5 }[/math] |
| M24 | Mathieu | 1861 | 1 1st | align=right | 244823040 | ≈ 2×108 | 210 × 33 × 5 × 7 × 11 × 23 | 23 | 2B, 3A, 23 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(ab(abab^2)^2 ab^2\bigr) = 4 }[/math] |
| M23 | Mathieu | 1861 | 1 1st | align=right | 10200960 | ≈ 1×107 | 27 × 32 × 5 × 7 × 11 × 23 | 22 | 2, 4, 23 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^2 (abab^2)^2 ab^2\bigr) = 8 }[/math] |
| M22 | Mathieu | 1861 | 1 1st | align=right |443520 | ≈ 4×105 | 27 × 32 × 5 × 7 × 11 | 21 | 2A, 4A, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl(abab^2\bigr) = 11 }[/math] |
| M12 | Mathieu | 1861 | 1 1st | align=right |95040 | ≈ 1×105 | 26 × 33 × 5 × 11 | 11 | 2B, 3B, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl([a,b]\bigr) = o\bigl(ababab^{2}\bigr) = 6 }[/math] |
| M11 | Mathieu | 1861 | 1 1st | align=right |7920 | ≈ 8×103 | 24 × 32 × 5 × 11 | 10 | 2, 4, 11 | [math]\displaystyle{ o\bigl((ab)^2 (abab^2)^2 ab^2\bigr) = 4 }[/math] |
Notes
- ↑ The groups of prime order, the alternating groups of degree at least 5, the infinite family of commutator groups 2F4(22n+1)′ of groups of Lie type (containing the Tits group), and 15 families of groups of Lie type.
- ↑ (Conway Curtis) organizes the 26 sporadic groups in likeness:
- "The sporadic simple groups may be roughly sorted as the Mathieu groups, the Leech lattice groups, Fischer's 3-transposition groups, the further Monster centralizers, and the half-dozen oddments."
- ↑ Here listed are semi-presentations from standard generators of each sporadic group. Most sporadic groups have multiple presentations & semi-presentations; the more prominent examples are listed.
- ↑ Where [math]\displaystyle{ u = (b^{2}(b^{2})abb)^{3} }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ v = t(b^{2}(b^{2})t)^{2} }[/math] with [math]\displaystyle{ t = abab^{3}a^{2} }[/math].
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 (Conway Curtis)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1998)
- ↑ (Gorenstein Lyons)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 (Ronan 2006)
- ↑ (Howlett Rylands)
- "This completes the determination of matrix generators for all groups of Lie type, including the twisted groups of Steinberg, Suzuki and Ree (and the Tits group)."
- ↑ (Gorenstein 1979)
- ↑ (Conway Curtis)
- ↑ (Hartley Hulpke)
- "The finite simple groups are the building blocks of finite group theory. Most fall into a few infinite families of groups, but there are 26 (or 27 if the Tits group 2F4(2)′ is counted also) which these infinite families do not include."
- ↑ (Wilson Parker)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1982)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1998)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1998)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1998)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1982)
- ↑ (Griess, Jr. 1998)
- ↑ (Hiss 2003)
- Tabelle 2. Die Entdeckung der sporadischen Gruppen (Table 2. The discovery of the sporadic groups)
- ↑ (Sloane 1996)
- ↑ (Jansen 2005)
- ↑ (Nickerson Wilson)
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 (Wilson Parker)
- ↑ (Lubeck 2001)
Works cited
- Burnside, William (1911). Theory of groups of finite order (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. xxiv, 1–512. doi:10.1112/PLMS/S2-7.1.1. ISBN 0-486-49575-2. OCLC 54407807.
- Conway, J. H. (1968). "A perfect group of order 8,315,553,613,086,720,000 and the sporadic simple groups". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 61 (2): 398–400. doi:10.1073/pnas.61.2.398. PMID 16591697. Bibcode: 1968PNAS...61..398C.
- Conway, J. H.; Curtis, R. T.; Norton, S. P.; Parker, R. A.; Wilson, R. A. (1985). ATLAS of Finite Groups: Maximal Subgroups and Ordinary Characters for Simple Groups. Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp. xxxiii; 1–252. ISBN 978-0-19-853199-9. OCLC 12106933.
- Gorenstein, D. (1979). "The classification of finite simple groups. I. Simple groups and local analysis". Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society. New Series (American Mathematical Society) 1 (1): 43–199. doi:10.1090/S0273-0979-1979-14551-8.
- Gorenstein, D.; Lyons, Richard; Solomon, Ronald (1998). The classification of the finite simple groups, Number 3. Mathematical Surveys and Monographs. 40. Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society. pp. xiii, 1–362. doi:10.1112/S0024609398255457. ISBN 978-0-8218-0391-2. OCLC 6907721813. https://bookstore.ams.org/surv-40-3/.
- Griess, Jr., Robert L. (1982). "The Friendly Giant". Inventiones Mathematicae 69: 1−102. doi:10.1007/BF01389186. Bibcode: 1982InMat..69....1G. https://www.digizeitschriften.de/dms/img/?PPN=PPN356556735_0069&DMDID=dmdlog7.
- Griess, Jr., Robert L. (1998). Twelve Sporadic Groups. Springer Monographs in Mathematics. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 1−169. ISBN 9783540627784. OCLC 38910263.
- Hartley, Michael I.; Hulpke, Alexander (2010), "Polytopes Derived from Sporadic Simple Groups", Contributions to Discrete Mathematics (Alberta, CA: University of Calgary Department of Mathematics and Statistics) 5 (2): 106−118, doi:10.11575/cdm.v5i2.61945, ISSN 1715-0868, https://cdm.ucalgary.ca/article/view/61945/46662
- Hiss, Gerhard (2003). "Die Sporadischen Gruppen (The Sporadic Groups)". Jahresber. Deutsch. Math.-Verein. (Annual Report of the German Mathematicians Association) 105 (4): 169−193. ISSN 0012-0456. https://www.mathematik.de/images/DMV/Jahresberichte/Jahresberichte_Archiv/Jahresbericht_04-2003.pdf. (German)
- Howlett, R. B.; Rylands, L. J.; Taylor, D. E. (2001). "Matrix generators for exceptional groups of Lie type". Journal of Symbolic Computation 31 (4): 429–445. doi:10.1006/jsco.2000.0431.
- Jansen, Christoph (2005). "The Minimal Degrees of Faithful Representations of the Sporadic Simple Groups and their Covering Groups". LMS Journal of Computation and Mathematics (London Mathematical Society) 8: 122−144. doi:10.1112/S1461157000000930.
- Lubeck, Frank (2001). "Smallest degrees of representations of exceptional groups of Lie type". Communications in Algebra (Philadelphia, PA: Taylor & Francis) 29 (5): 2147−2169. doi:10.1081/AGB-100002175. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1081/AGB-100002175.
- Nickerson, S.J.; Wilson, R.A. (2011). "Semi-Presentations for the Sporadic Simple Groups". Experimental Mathematics (Oxfordshire: Taylor & Francis) 14 (3): 359−371. doi:10.1080/10586458.2005.10128927. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10586458.2005.10128927.
- Ronan, Mark (2006). Symmetry and the Monster: One of the Greatest Quests of Mathematics. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. vii, 1–255. ISBN 978-0-19-280722-9. OCLC 180766312. https://archive.org/details/symmetrymonstero0000rona.
- Sloane, N. J. A., ed (1996). "Orders of sporadic simple groups (A001228)". OEIS Foundation. http://oeis.org/A001228.
- Wilson, R.A (1998). "Chapter: An Atlas of Sporadic Group Representations". The Atlas of Finite Groups - Ten Years On (LMS Lecture Note Series 249). Cambridge, U.K: Cambridge University Press. pp. 261–273. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511565830.024. ISBN 9780511565830. OCLC 726827806. https://webspace.maths.qmul.ac.uk/r.a.wilson/pubs_files/ASGRweb.pdf.
- Wilson, R.A.; Parker, R.A.; Nickerson, S.J.; Bray, J.N. (1999). "ATLAS of Group Representations". Queen Mary University of London. https://brauer.maths.qmul.ac.uk/Atlas/.
External links
- Atlas of Finite Group Representations: Sporadic groups
- Weisstein, Eric W.. "Sporadic Group". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/SporadicGroup.html.
he:משפט המיון לחבורות פשוטות סופיות
 |

