Plastic number
Template:Infobox non-integer number
In mathematics, the plastic number ρ (also known as the plastic constant, the plastic ratio, the minimal Pisot number, the platin number,[1] Siegel's number or, in French, le nombre radiant) is a mathematical constant which is the unique real solution of the cubic equation
- [math]\displaystyle{ x^3 = x + 1. }[/math]
It has the exact value[2]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \rho = \sqrt[3]{\frac{9+\sqrt{69}}{18}}+\sqrt[3]{\frac{9-\sqrt{69}}{18}}. }[/math]
Its decimal expansion begins with 1.324717957244746025960908854....[3]
Properties
Recurrences
The powers of the plastic number A(n) = ρn satisfy the third-order linear recurrence relation A(n) = A(n − 2) + A(n − 3) for n > 2. Hence it is the limiting ratio of successive terms of any (non-zero) integer sequence satisfying this recurrence such as the Padovan sequence (also known as the Cordonnier numbers), the Perrin numbers and the Van der Laan numbers,[4] and bears relationships to these sequences akin to the relationships of the golden ratio to the second-order Fibonacci and Lucas numbers, akin to the relationships between the silver ratio and the Pell numbers.[5]
The plastic number satisfies the nested radical recurrence[6]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \rho = \sqrt[3]{1 + \sqrt[3]{1 + \sqrt[3]{1 + \cdots}}}. }[/math]
Number theory
Because the plastic number has the minimal polynomial x3 − x − 1 = 0, it is also a solution of the polynomial equation p(x) = 0 for every polynomial p that is a multiple of x3 − x − 1, but not for any other polynomials with integer coefficients. Since the discriminant of its minimal polynomial is −23, its splitting field over rationals is [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{Q}(\sqrt{-23}, \rho). }[/math] This field is also a Hilbert class field of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbb{Q}(\sqrt{-23}). }[/math] As such, it can be expressed[6] in terms of the Dedekind eta function [math]\displaystyle{ \eta(\tau) }[/math] with argument [math]\displaystyle{ \tau = \tfrac{1+\sqrt{-23}}2 }[/math],
- [math]\displaystyle{ \rho= \frac{-1}{z^{23}}\frac{\eta(\tau)}{\sqrt2\,\eta(2\tau)} = 1.3247\dots }[/math]
and root of unity [math]\displaystyle{ z = e^{2\pi i/48} }[/math]. Similarly, for the supergolden ratio with argument [math]\displaystyle{ \beta = \tfrac{1+\sqrt{-31}}2 }[/math],
- [math]\displaystyle{ \psi= \frac{-1}{z^{23}}\frac{\eta(\beta)}{\sqrt2\,\eta(2\beta)} = 1.4655\dots }[/math]
Also, the plastic number is the smallest Pisot–Vijayaraghavan number. Its algebraic conjugates are
- [math]\displaystyle{ \left(-\frac12 \pm \frac{\sqrt3}{2}i\right) \sqrt[3]{\frac{9 + \sqrt{69}}{18}} + \left(-\frac12 \mp \frac{\sqrt3}{2}i\right) \sqrt[3]{\frac{9 - \sqrt{69}}{18}} \approx -0.662359 \pm 0.56228i, }[/math]
of absolute value ≈ 0.868837 (sequence A191909 in the OEIS). This value is also [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\sqrt{\rho}} }[/math] because the product of the three roots of the minimal polynomial is 1.
Trigonometry
The plastic number can be written using the hyperbolic cosine (cosh) and its inverse:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \rho = \frac{2\sqrt{3}}{3} \cosh\left(\frac{1}{3} \cosh^{-1} \left(\frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)\right). }[/math]
(See Cubic function.)
Geometry
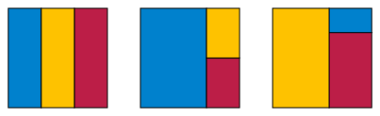
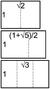
There are precisely three ways of partitioning a square into three similar rectangles:[7]Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag[8]
History and names
Dutch architect and Benedictine monk Dom Hans van der Laan gave the name plastic number (Dutch: het plastische getal) to this number in 1928. In 1924, four years prior to van der Laan's naming, French engineer Gérard Cordonnier (fr) had already discovered the number and referred to it as the radiant number (French: le nombre radiant). Unlike the names of the golden ratio and silver ratio, the word plastic was not intended by van der Laan to refer to a specific substance, but rather in its adjectival sense, meaning something that can be given a three-dimensional shape.[9] This, according to Richard Padovan, is because the characteristic ratios of the number, 3/4 and 1/7, relate to the limits of human perception in relating one physical size to another. Van der Laan designed the 1967 St. Benedictusberg Abbey church to these plastic number proportions.[10]
The plastic number is also sometimes called the silver number, a name given to it by Midhat J. Gazalé[11] and subsequently used by Martin Gardner,[12] but that name is more commonly used for the silver ratio [math]\displaystyle{ 1 + \sqrt{2}, }[/math] one of the ratios from the family of metallic means first described by Vera W. de Spinadel in 1998.[13]
Martin Gardner has suggested referring to [math]\displaystyle{ \rho^2 }[/math] as "high phi", and Donald Knuth created a special typographic mark for this name, a variant of the Greek letter phi ("φ") with its central circle raised, resembling the Georgian letter pari ("Ⴔ").[14]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Choulet, Richard (January–February 2010), "Alors argent ou pas ? Euh ... je serais assez platine", Le Bulletin Vert (Association des Professeurs de Mathématiques de l'Enseignement Public (APMEP) Paris) (486): 89–96, ISSN 0240-5709, OCLC 477016293, http://www.apmep.fr/IMG/pdf/AAA10014.pdf, retrieved 2017-11-14
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Plastic Constant". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/PlasticConstant.html.
- ↑ Sequence OEIS: A060006 in the OEIS.
- ↑ Sloane, N. J. A., ed. "Sequence A182097 (Van der Laan numbers)". OEIS Foundation. https://oeis.org/A182097.
- ↑ (Shannon Anderson).
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Piezas, Tito III. "Plastic Constant". http://mathworld.wolfram.com/PlasticConstant.html.
- ↑ Ian Stewart, A Guide to Computer Dating (Feedback), Scientific American, Vol. 275, No. 5, November 1996, p. 118
- ↑ Laczkovich, M. (1995), "Tilings of the square with similar rectangles", Discrete & Computational Geometry 13 (3–4): 569–572, doi:10.1007/BF02574063
- ↑ (Padovan 2002); (Shannon Anderson).
- ↑ (Padovan 2002).
- ↑ Gazalé, Midhat J. (April 19, 1999), "Chapter VII: The Silver Number", Gnomon: From Pharaohs to Fractals, Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, pp. 135–150, ISBN 9780691005140, OCLC 40298400
- ↑ Martin Gardner, A Gardner's Workout (2001), Chapter 16, pp. 121–128.
- ↑ de Spinadel, Vera W. (1998), Williams, Kim, ed., "The Metallic Means and Design", Nexus II: Architecture and Mathematics (Fucecchio (Florence): Edizioni dell'Erba): 141–157, https://www.nexusjournal.com/the-nexus-conferences/nexus-1998/119-n1998-spinadel.html
- ↑ "Six challenging dissection tasks", Quantum 4 (5): 26–27, May–June 1994, http://static.nsta.org/pdfs/QuantumV4N5.pdf
References
- Aarts, J.; Fokkink, R.; Kruijtzer, G. (2001), "Morphic numbers", Nieuw Arch. Wiskd., 5 2 (1): 56–58, http://www.nieuwarchief.nl/serie5/pdf/naw5-2001-02-1-056.pdf.
- Gazalé, Midhat J. (1999), Gnomon, Princeton University Press.
- "Dom Hans Van Der Laan And The Plastic Number", Nexus IV: Architecture and Mathematics, Kim Williams Books, 2002, pp. 181–193, http://www.nexusjournal.com/conferences/N2002-Padovan.html.
- Shannon, A. G.; Anderson, P. G.; Horadam, A. F. (2006), "Properties of Cordonnier, Perrin and Van der Laan numbers", International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology 37 (7): 825–831, doi:10.1080/00207390600712554.
External links
- Tales of a Neglected Number by Ian Stewart
- Plastic rectangle and Padovan sequence at Tartapelago by Giorgio Pietrocola