Neural Turing machine
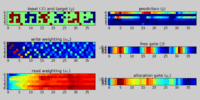
A Neural Turing machine (NTMs) is a recurrent neural network model of a Turing machine. The approach was published by Alex Graves et al. in 2014.[1] NTMs combine the fuzzy pattern matching capabilities of neural networks with the algorithmic power of programmable computers. An NTM has a neural network controller coupled to external memory resources, which it interacts with through attentional mechanisms. The memory interactions are differentiable end-to-end, making it possible to optimize them using gradient descent.[2] An NTM with a long short-term memory (LSTM) network controller can infer simple algorithms such as copying, sorting, and associative recall from examples alone.[1]
The authors of the original NTM paper did not publish their source code.[1] The first stable open-source implementation was published in 2018 at the 27th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, receiving a best-paper award. [3][4][5] Other open source implementations of NTMs exist but as of 2018 they are not sufficiently stable for production use.[6][7][8][9][10][11][12] The developers either report that the gradients of their implementation sometimes become NaN during training for unknown reasons and cause training to fail;[10][11][9] report slow convergence;[7][6] or do not report the speed of learning of their implementation.[12][8]
Differentiable neural computers are an outgrowth of Neural Turing machines, with attention mechanisms that control where the memory is active, and improve performance.[13]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Graves, Alex; Wayne, Greg; Danihelka, Ivo (2014). "Neural Turing Machines". arXiv:1410.5401 [cs.NE].
- ↑ "Deep Minds: An Interview with Google's Alex Graves & Koray Kavukcuoglu". https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/deep-minds-interview-googles-alex-graves-koray-sophie-curtis.
- ↑ Collier, Mark; Beel, Joeran (2018), "Implementing Neural Turing Machines" (in en), Artificial Neural Networks and Machine Learning – ICANN 2018 (Springer International Publishing): pp. 94–104, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-01424-7_10, ISBN 9783030014230, Bibcode: 2018arXiv180708518C
- ↑ "MarkPKCollier/NeuralTuringMachine" (in en). https://github.com/MarkPKCollier/NeuralTuringMachine.
- ↑ Beel, Joeran (2018-10-20). "Best-Paper Award for our Publication "Implementing Neural Turing Machines" at the 27th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks | Prof. Joeran Beel (TCD Dublin)" (in en-GB). Trinity College Dublin, School of Computer Science and Statistics Blog. https://www.scss.tcd.ie/joeran.beel/blog/2018/10/20/best-paper-award-for-our-publication-implementing-neural-turing-machines-at-icann-conference/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "snowkylin/ntm" (in en). https://github.com/snowkylin/ntm.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "chiggum/Neural-Turing-Machines" (in en). https://github.com/chiggum/Neural-Turing-Machines.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "yeoedward/Neural-Turing-Machine" (in en). 2017-09-13. https://github.com/yeoedward/Neural-Turing-Machine.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "camigord/Neural-Turing-Machine" (in en). https://github.com/camigord/Neural-Turing-Machine.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "carpedm20/NTM-tensorflow" (in en). https://github.com/carpedm20/NTM-tensorflow.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 "snipsco/ntm-lasagne" (in en). https://github.com/snipsco/ntm-lasagne.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "loudinthecloud/pytorch-ntm" (in en). https://github.com/loudinthecloud/pytorch-ntm.
- ↑ Administrator. "DeepMind's Differentiable Neural Network Thinks Deeply". http://www.i-programmer.info/news/105-artificial-intelligence/10174-deepminds-differential-nn-thinks-deeply.html.