Medicine:Acrocephalosyndactylia
From HandWiki
| Acrocephalosyndactylia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ACS[1] |
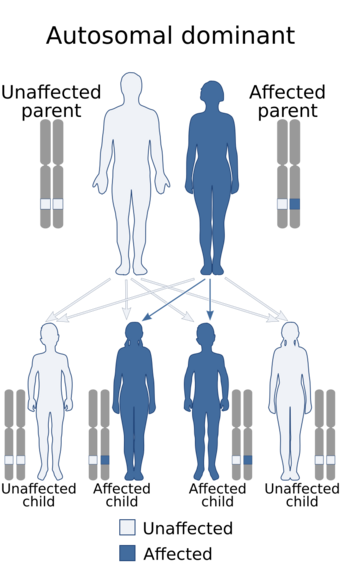 | |
| Acrocephalosyndactylia is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner | |
In pediatric medicine, acrocephalosyndactylia (or acrocephalosyndactyly) is the common presentation of craniosynostosis and syndactyly.[2]
Cause
Diagnosis
Classification
It has several different types:
- type 1 – Apert syndrome[3][4]:577
- type 2 – Crouzon syndrome[4]:577[5]
- type 3 – Saethre–Chotzen syndrome[citation needed]
- type 4 - Goodman Syndrome[6]
- type 5 – Pfeiffer syndrome[7][8]
A related term, "acrocephalopolysyndactyly" (ACPS), refers to the inclusion of polydactyly to the presentation. It also has multiple types:
- type 1 – Noack syndrome; now classified with Pfeiffer syndrome[8]
- type 2 – Carpenter syndrome[9]
- type 3 – Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale syndrome[10]
- type 4 – Goodman syndrome;[11][12] now classified with Carpenter syndrome[13]
- type 5 – Pfeiffer syndrome[citation needed]
It has been suggested that the distinction between "acrocephalosyndactyly" versus "acrocephalopolysyndactyly" should be abandoned.[14]
Treatment
See also
- List of skin conditions
- Oxycephaly
References
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Acrocephalosyndactyly" (in en). https://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/OC_Exp.php?lng=en&Expert=946. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- ↑ "A case of acrocephalosyndactyly with low imperforate anus". J. Pediatr. Surg. 39 (1): E32–4. January 2004. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2003.09.037. PMID 14694405.
- ↑ DDB Apert syndrome
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. ISBN:0-7216-2921-0.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Apert syndrome -101200
- ↑ DDB Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
- ↑ DDB Pfeiffer syndrome
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Pfeiffer syndrome -101600
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Carpenter syndrome -201000
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Acrocephalopolysyndactyly type III -101120
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) Acrocephalopolysyndactyly type IV -201020
- ↑ "Acrocephalopolysyndactyly type IV: a new genetic syndrome in 3 sibs". Clin. Genet. 15 (3): 209–14. March 1979. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb00969.x. PMID 421359.
- ↑ "Acrocephalopolysyndactyly type II--Carpenter syndrome: clinical spectrum and an attempt at unification with Goodman and Summit syndromes". Am. J. Med. Genet. 28 (2): 311–24. October 1987. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320280208. PMID 3322002.
- ↑ "Hands and feet in the Apert syndrome". Am. J. Med. Genet. 57 (1): 82–96. May 1995. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320570119. PMID 7645606.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Acrocephalosyndactylia at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)

