List of spirals
From HandWiki
This list of spirals includes named spirals that have been described mathematically.
| Image | Name | First described | Equation | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circle | [math]\displaystyle{ r= k }[/math] | The trivial spiral | |||
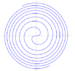
| Archimedean spiral (also arithmetic spiral) | -300 c. 320 BC | [math]\displaystyle{ r=a+b \cdot \theta }[/math] | |||
| Fermat's spiral (also parabolic spiral) | 1636[1] | [math]\displaystyle{ r^{2} = a^{2} \cdot \theta }[/math] | |||
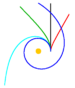
| Euler spiral (also Cornu spiral or polynomial spiral) | 1696[2] | [math]\displaystyle{ x(t) = \operatorname{C}(t),\, }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ y(t) = \operatorname{S}(t) }[/math] | using Fresnel integrals[3] | ||
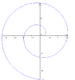
| hyperbolic spiral (also reciprocal spiral) | 1704 | [math]\displaystyle{ r = \frac{a}{\theta} }[/math] | |||
| lituus | 1722 | [math]\displaystyle{ r^{2} \cdot \theta = k }[/math] | |||
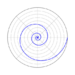
| logarithmic spiral (also known as equiangular spiral) | 1638[4] | [math]\displaystyle{ r=a\cdot e^{b \cdot \theta} }[/math] | Approximations of this are found in nature | ||
| Fibonacci spiral | circular arcs connecting the opposite corners of squares in the Fibonacci tiling | approximation of the golden spiral | |||
| golden spiral | [math]\displaystyle{ r = \varphi^{\frac{2 \cdot \theta}{\pi}}\, }[/math] | special case of the logarithmic spiral | |||
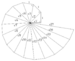
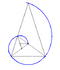
| Spiral of Theodorus (also known as Pythagorean spiral) | c. 500 BC | contiguous right triangles composed of one leg with unit length and the other leg being the hypotenuse of the prior triangle | approximates the Archimedean spiral | ||
| involute | 1673 | [math]\displaystyle{ x(t)=r(\cos(t+a)+t\sin(t+a)), }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ y(t)=r(\sin(t+a)-t \cos(t+a)) }[/math] |
involutes of a circle appear like Archimedean spirals | ||
| helix | [math]\displaystyle{ r(t) = 1,\, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ \theta(t) = t,\, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ z(t) = t }[/math] | a 3-dimensional spiral | |||
| Rhumb line (also loxodrome) | type of spiral drawn on a sphere | ||||
| Cotes's spiral | 1722 | [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{r} = \begin{cases} A \cosh(k\theta + \varepsilon) \\ A \exp(k\theta + \varepsilon) \\ A \sinh(k\theta + \varepsilon) \\ A (k\theta + \varepsilon) \\ A \cos(k\theta + \varepsilon) \\ \end{cases} }[/math] | Solution to the two-body problem for an inverse-cube central force | ||
| Poinsot's spirals | [math]\displaystyle{ r = a \cdot \operatorname{csch}(n \cdot \theta),\, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ r = a \cdot \operatorname{sech}(n \cdot \theta) }[/math] |
||||
| Nielsen's spiral | 1993[5] | [math]\displaystyle{ x(t) = \operatorname{ci}(t),\, }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ y(t) = \operatorname{si}(t) }[/math] |
A variation of Euler spiral, using sine integral and cosine integrals | ||
| Polygonal spiral | special case approximation of logarithmic spiral | ||||
| Fraser's Spiral | 1908 | Optical illusion based on spirals | |||
| Conchospiral | [math]\displaystyle{ r = \mu^{t} \cdot a,\, }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ \theta = t,\, }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ z = \mu^{t} \cdot c }[/math] | three-dimensional spiral on the surface of a cone. | |||
| Calkin–Wilf spiral | |||||
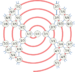
| Ulam spiral (also prime spiral) | 1963 | ||||
| Sack's spiral | 1994 | variant of Ulam spiral and Archimedean spiral. | |||
| Seiffert's spiral | 2000[6] | [math]\displaystyle{ r = \operatorname{sn}(s, k),\, }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ \theta = k \cdot s }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ z = \operatorname{cn}(s, k) }[/math] | spiral curve on the surface of a sphere
using the Jacobi elliptic functions[7] | ||
| Tractrix spiral | 1704[8] | [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{cases} r = A \cos(t) \\ \theta = \tan(t ) -t\end{cases} }[/math] | |||
| Pappus spiral | 1779 | [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{cases} r=a \theta \\ \psi = k \end{cases} }[/math] | 3D conical spiral studied by Pappus and Pascal[9] | ||
| doppler spiral | [math]\displaystyle{ x = a \cdot ( t \cdot \cos(t) + k \cdot t),\, }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ y = a \cdot t \cdot \sin(t) }[/math] | 2D projection of Pappus spiral[10] | |||
| Atzema spiral | [math]\displaystyle{ x = \frac{\sin(t)}{t} - 2 \cdot \cos(t) - t \cdot \sin(t),\, }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ y = -\frac{\cos(t)}{t} - 2 \cdot \sin(t) + t \cdot \cos(t) }[/math] | The curve that has a catacaustic forming a circle. Approximates the Archimedean spiral.[11] | |||
| Atomic spiral | 2002 | [math]\displaystyle{ r = \frac{\theta}{\theta - a} }[/math] | This spiral has two asymptotes; one is the circle of radius 1 and the other is the line [math]\displaystyle{ \theta=a }[/math][12] | ||
| Galactic spiral | 2019 | [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{cases} dx=R \cdot \frac{y}{\sqrt{x^2 +y^2}} d\theta \\ dy=R \cdot \left[\rho(\theta)- \frac{x}{\sqrt{x^2+y^2}} \right] d\theta \end{cases} \begin{cases} x= \sum dx \\ \\ \\ y= \sum dy + R \end{cases} }[/math] | The differential spiral equations were developed to simulate the spiral arms of disc galaxies, have 4 solutions with three different cases:[math]\displaystyle{ \rho \lt 1, \rho = 1, \rho \gt 1 }[/math], the spiral patterns are decided by the behavior of the parameter [math]\displaystyle{ \rho }[/math]. For [math]\displaystyle{ \rho \lt 1 }[/math], spiral-ring pattern; [math]\displaystyle{ \rho = 1, }[/math] regular spiral; [math]\displaystyle{ \rho \gt 1, }[/math] loose spiral. R is the distance of spiral starting point (0, R) to the center. The calculated x and y have to be rotated backward by ([math]\displaystyle{ -\theta }[/math]) for plotting.[13] |
See also
- Catherine wheel (firework)
- List of spiral galaxies
- Parker spiral
- Spirangle
- Spirograph
References
- ↑ "Fermat spiral - Encyclopedia of Mathematics". https://www.encyclopediaofmath.org/index.php/Fermat_spiral. Retrieved 18 February 2019.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Cornu Spiral" (in en). https://mathworld.wolfram.com/.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Fresnel Integrals" (in en). https://mathworld.wolfram.com/.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Logarithmic Spiral" (in en). Wolfram Research, Inc.. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/LogarithmicSpiral.html. Retrieved 18 February 2019.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Nielsen's Spiral" (in en). Wolfram Research, Inc.. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/NielsensSpiral.html. Retrieved 18 February 2019.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Seiffert's Spherical Spiral" (in en). https://mathworld.wolfram.com/.
- ↑ Weisstein, Eric W.. "Seiffert's Spherical Spiral" (in en). https://mathworld.wolfram.com/.
- ↑ "Tractrix spiral". http://www.mathcurve.com/courbes2d.gb/spiraletractrice/spiraletractrice.shtml.
- ↑ "Conical spiral of Pappus". https://www.mathcurve.com/courbes3d.gb/spiraleconic/pappus.shtml. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- ↑ "Doppler spiral". https://www.mathcurve.com/courbes2d.gb/doppler/doppler.htm. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- ↑ "Atzema spiral". http://www.2dcurves.com/spiral/spiralat.html. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ↑ "atom-spiral". http://www.2dcurves.com/spiral/spiralas.html. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ↑ Pan, Hongjun. "New spiral". https://arpgweb.com/pdf-files/ajams7(2)66-76.pdf. Retrieved 5 March 2021.
 |