Chemistry:Phosphoryl fluoride
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Phosphoryl trifluoride
Phosphorus trifluoride oxide | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
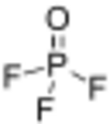
| POF 3 | |||
| Molar mass | 103.9684 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colourless gas | ||
| Boiling point | −39.7 °C (−39.5 °F; 233.5 K) | ||
| Reacts | |||
| Solubility | Reacts with alcohol and acid, soluble in diethyl ether and hydrocarbons | ||
| 1.76 D[1] | |||
| Structure | |||
| Tetrahedral at the P atom | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Poison, corrosive, can form HF on contact with H 2O | ||
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0190 | ||
| GHS pictograms |    
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H302, H314, H330, H372 | |||
| P260, P264, P270, P271, P280, P284, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P314, P320, P321, P330, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Phosphoryl fluoride (commonly called phosphorus oxyfluoride) is a compound with the chemical formula POF
3. It is a colorless gas that hydrolyzes rapidly. It has a critical temperature of 73 °C and a
critical pressure of 4.25 bars.[1]
Synthesis and reactions
Phosphorus oxyfluoride is prepared by partial hydrolysis of phosphorus pentafluoride.
Phosphorus oxyfluoride is the progenitor of the simple fluorophosphoric acids by hydrolysis. The sequence starts with difluorophosphoric acid:
- POF
3 + H
2O → HPO
2F
2 + HF
The next steps give monofluorophosphoric acid and phosphoric acid:
- HPO
2F
2 + H
2O → H
2PO
3F + HF - H
2PO
3F + H
2O → H
3PO
4 + HF
Phosphoryl fluoride combines with dimethylamine to produce dimethylaminophosphoryl difluoride (H
3C–)
2N–P(=O)F
2 and difluorophosphate and hexafluorophosphate ions.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Phosphoryl fluoride". https://www.stenutz.eu/chem/solv6.php?name=phosphoryl+fluoride.
- ↑ Cavell, R. G. (1968). "Chemistry of phosphorus fluorides. Part III. The reaction of thiophosphoryl-fluoride with dimethylamine and some properties of the dimethylaminothio- phosphoryl fluorides". Canadian Journal of Chemistry 46 (4): 613. doi:10.1139/v68-100.
 |