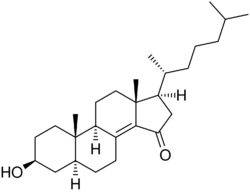
Chemistry:Colestolone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 5α-Cholest-8(14)-en-3β-ol-15-one; 3β-Hydroxy-5α-cholest-8(14)-en-15-one |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C27H44O2 |
| Molar mass | 400.647 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Colestolone (INN, USAN), also known as 5α-cholest-8(14)-en-3β-ol-15-one, is a potent inhibitor of sterol biosynthesis which is described as a hypocholesterolemic (lipid-lowering) agent.[1][2][3][4][5] It was first reported in 1977 and was studied until at least 1988, but was never introduced for medical use.[1][3][4]
Colestolone has been found to significantly reduce serum levels of cholesterol both in animals and in humans.[3][4][5] It inhibits multiple relatively early-stage steps in cholesterol biosynthesis such as HMG-CoA reductase[6] and does not appear to affect any late-stage steps (after squalene, specifically).[5] Unlike late-stage cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors like triparanol and azacosterol, no accumulation of sterols has been observed in animals treated with colestolone, suggesting that it does not share the toxicity of late-stage cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors.[5]
In addition to its potent inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis, it is notable that colestolone also happens to serve as a precursor of cholesterol, and is efficiently converted into it in rat liver homogenates and upon oral administration to rats.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 646–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=0vXTBwAAQBAJ&pg=PA646.
- ↑ Daniel Lednicer (4 March 2009). Strategies for Organic Drug Synthesis and Design. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 186–. ISBN 978-0-470-39959-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=fEwl6Qev-mUC&pg=PA186.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "9α-hydroxy-3-oxo-4,24(25)-stigmastadien-26-oic acid derivatives, a process for preparing same and pharmaceutical compositions containing same". https://www.google.com/patents/US5112815.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Inhibitors of sterol synthesis. Metabolism of 5 alpha-cholest-8(14)-en-3 beta-ol-15-one after intravenous administration to bile duct-cannulated rats". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (9): 4110–23. 1988. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)68897-0. PMID 3346239.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 "5 alpha-Cholest-8(14)-en-3 beta-ol-15-one, a potent inhibitor of sterol biosynthesis, lowers serum cholesterol and alters distributions of cholesterol in lipoproteins in baboons". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79 (9): 3042–6. 1982. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.9.3042. PMID 6953447. Bibcode: 1982PNAS...79.3042S.
- ↑ Pharmaceutical R&D costs, risks, and rewards.. DIANE Publishing. 1993. pp. 25–. ISBN 978-1-4289-2103-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=Jh49Llr2x0AC&pg=PA25.
 |

