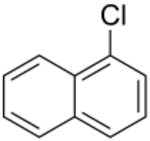
Chemistry:1-Chloronaphthalene
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Chloronaphthalene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H7Cl | |
| Molar mass | 162.62 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K) |
| Boiling point | 263 °C (505 °F; 536 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | Oxford MSDS |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | WARNING |
| H302, H410 | |
| P273 | |
| Flash point | 121 °C (250 °F; 394 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Chloronaphthalene is an aromatic compound. It is a colorless, oily liquid which may be used to determine the refractive index of crystals by immersion.[1] The compound is an isomer to 2-chloronaphthalene.
Synthesis
1-Chloronaphthalene is obtained directly by chlorination of naphthalene, with the formation of more highly substituted derivatives such as dichloro- and trichloronaphthalenes in addition to the two monochlorinated isomeric compounds: 1-chloronaphthalene and 2-chloronaphthalene.[2]
Applications
This toxic, nonpolar organochlorine compound is sometimes used as a powerful biocide, and is also known as Basileum. It occasionally serves as insecticide and fungicide in the timber floors of shipping containers, where it fulfills the same role as chlordane.
1-Chloronaphthalene was also used as a common solvent[3] for oils, fats and DDT until the 1970s. It is also used to determine the refractive index of crystals.
See also
References
- ↑ "Oxford MSDS". http://msds.chem.ox.ac.uk/CH/1-chloronaphthalene.html.
- ↑ Bavendamm, W.; Bellmann, H. (1953). "Chlornaphthalin-Präparate" (in German). Holz Als Roh- und Werkstoff 11 (2): 81–84. doi:10.1007/BF02605462.
- ↑ "1-Chloronaphthalene". sigmaaldrich.com. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sial/25320?lang=en®ion=RU. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
 |

