Chemistry:1,5-Diaminonaphthalene
From HandWiki
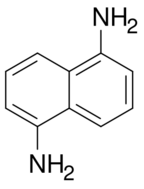
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Naphthalene-1,5-diamine | |
| Other names
Alphamin, 1,5-DAN
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3077 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10N2 | |
| Molar mass | 158.204 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.4 |
| Melting point | 185–187 °C (365–369 °F; 458–460 K) |
| Structure[1] | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/c | |
a = 5.1790, b = 11.008, c = 21.238 α = 90°, β = 90.68°, γ = 90°[2]
| |
Lattice volume (V)
|
1210.7 |
Formula units (Z)
|
6 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H351, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P273, P281, P308+313, P391, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 226 °C (439 °F; 499 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1,5-Diaminonaphthalene is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(NH2)2. It is one of several diaminonaphthalenes. It is a colorless solid that darkens in air due to oxidation.
Synthesis and reactions
It is prepared by reduction of 1,5-dinitronaphthalene, which in turn is obtained with the 1,8-isomers by nitration of 1-nitronaphthalene. It can also be prepared by treatment of 1,5-dihydroxynaphthalene with ammonium sulfite. It is a precursor to naphthalene-1,5-diisocyanate, a precursor to specialty polyurethanes.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Bernes, S.; Pastrana, M.R.; Sanchez, E.H.; Perez, R.G. (2004). "Crystal Structure". CCDC 232143: Experimental Crystal Structure Determination. Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre. doi:10.5517/cc7skh1.
- ↑ Bernès, Sylvain; Pastrana, Modesto Rodríguez; Sánchez, Enrique Huerta; Pérez, René Gutiérrez (12 December 2003). "1,5-Diaminonaphthalene". Acta Crystallographica Section E 60 (1): o45–o47. doi:10.1107/S1600536803026643.
- ↑ Booth, Gerald (2005). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
 |

