Biology:Limnocyonidae
| Limnocyonidae | |
|---|---|
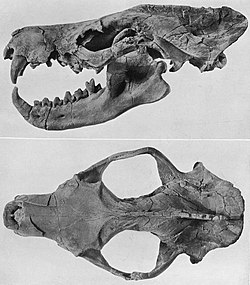
| |
| Skull of Limnocyon verus | |

| |
| lower jaw of Prolimnocyon antiquus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | †Hyaenodonta |
| Family: | †Hyaenodontidae |
| Subfamily: | †Limnocyoninae Wortman, 1902[1] |
| Type genus | |
| †Limnocyon Marsh, 1872
| |
| Genera | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
Limnocyonidae ("swamp dogs") is a family of extinct predatory mammals from extinct order Hyaenodonta. Fossil remains of these mammals are known from late Paleocene to late Eocene deposits in North America and Asia.[5] Limnocyonids had only two molars in the upper and lower dentition.[6]
Classification and phylogeny
Taxonomy
- Family: †Limnocyonidae (Wortman, 1902)
- Genus: †Iridodon (Morlo & Gunnell, 2003)
- †Iridodon datzae (Morlo & Gunnell, 2003)
- Genus: †Limnocyon (paraphyletic genus) (Marsh, 1872)
- †Limnocyon cuspidens (Morlo & Gunnell, 2005)
- †Limnocyon potens (Matthew, 1909)
- †Limnocyon verus (Marsh, 1872)
- Genus: †Oxyaenodon (Matthew, 1899)
- †Oxyaenodon dysodus (Matthew, 1899)
- Genus: †Prolaena (Xu, 1979)
- †Prolaena parva (Xu, 1979)
- Genus: †Prolimnocyon (paraphyletic genus) (Matthew & Granger, 1915)
- †Prolimnocyon antiquus (Matthew & Granger, 1915)
- †Prolimnocyon atavus (Matthew & Granger, 1915)
- †Prolimnocyon chowi (Meng, 1998)
- †Prolimnocyon eerius (Gingerich, 1989)
- †Prolimnocyon haematus (Gingerich & Deutsch, 1989)
- Genus: †Thinocyon (Marsh, 1872)
- †Thinocyon medius (Wortman, 1902)
- †Thinocyon velox (Marsh, 1872)
- Incertae sedis:
- †"Thinocyon" sichowensis (Chow, 1975)
- Genus: †Iridodon (Morlo & Gunnell, 2003)
Phylogeny
The phylogenetic relationships of family Limnocyonidae are shown in the following cladogram:[7][6][8][9][10][11][12]
| †Hyaenodonta |
|
Script error: No such module "Clade/labels". | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Mammal classification
- Hyaenodonta
References
- ↑ J. L. Wortman (1902.) "Studies of Eocene Mammalia in the Marsh Collection, Peabody Museum." The American Journal of Science, series 4 13:197-206
- ↑ L. Van Valen (1966.) "Deltatheridia, a new order of Mammals." Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History 132(1):1-126
- ↑ A. V. Lavrov (1999.) "Adaptive Radiation of Hyaenodontinae (Creodonta, Hyaenodontidae) of Asia." in 6th Congress of the Theriological Society, Moscow, April 13–16, p. 138 [in Russian].
- ↑ Savage, R. J. G. (1973). "Megistotherium, gigantic hyaenodont from Miocene of Gebel Zelten, Libya". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Geology 22 (7): 483–511. doi:10.5962/p.150151. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/36949982#page/661/mode/1up.
- ↑ McKenna, Malcolm C.; Bell, Susan K. (1997). Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level. New York: Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-11012-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=OLYifwU8bqQC&pg=PP9. Retrieved 16 March 2015.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 M. Morlo and G. F. Gunnell (2005.) "New species of Limnocyon (Mammalia, Creodonta) from the Bridgerian (middle Eocene)." Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 25(1):251-255
- ↑ M. Morlo & G. F. Gunnell (2003.) "Small Limnocyonines (Hyaenodontidae, Mammalia) From the Bridgerian Middle Eocene of Wyoming: Thinocyon, Prolimnocyon And Iridodon, New Genus." Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, University of Michigan 31(2):43-78
- ↑ Borths, Matthew R; Stevens, Nancy J (2017). "Deciduous dentition and dental eruption of Hyainailouroidea (Hyaenodonta, "Creodonta," Placentalia, Mammalia)". Palaeontologia Electronica 20 (3): 55A. doi:10.26879/776. http://palaeo-electronica.org/content/2017/2056-deciduous-hyaenodont-teeth.
- ↑ Matthew R. Borths; Nancy J. Stevens (2019). "Simbakubwa kutokaafrika, gen. et sp. nov. (Hyainailourinae, Hyaenodonta, 'Creodonta,' Mammalia), a gigantic carnivore from the earliest Miocene of Kenya". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 39 (1): e1570222. doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1570222. https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/8009951.
- ↑ Floréal Solé; Bernard Marandat; Fabrice Lihoreau (2020). "The hyaenodonts (Mammalia) from the French locality of Aumelas (Hérault), with possible new representatives from the late Ypresian". Geodiversitas 42 (13): 185–214. doi:10.5252/geodiversitas2020v42a13. http://sciencepress.mnhn.fr/en/periodiques/geodiversitas/42/13.
- ↑ Solé, F.; Morlo, M.; Schaal, T.; Lehmann, T. (2021). "New hyaenodonts (Mammalia) from the late Ypresian locality of Prémontré (France) support a radiation of the hyaenodonts in Europe already at the end of the early Eocene". Geobios 66-67: 119–141. doi:10.1016/j.geobios.2021.02.004.
- ↑ Averianov, Alexander; Obraztsova, Ekaterina; Danilov, Igor; Jin, Jian-Hua (2023). "A new hypercarnivorous hyaenodont from the Eocene of South China". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 11. doi:10.3389/fevo.2023.1076819. ISSN 2296-701X.

